What is a graphic editor definition. Graphic editor. Types and examples of graphic editors. Interface, features and tools of the graphic editor Paint
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
GOU VPO "Magnitogorsk State University".
Faculty of Fine Arts and Design.
Abstract on the topic:
"Types of graphic editors".
Magnitogorsk 2011
1. Introduction.
2. Types of graphic editors.
3. Basic functions of the graphic editor.
The cost of all other cost groups must be entered manually. If you want to add another apartment to your planning, select this menu item. After selecting it, a dialog box will appear in which you can specify the name of the apartment, as well as your own comments. After that, you can use both in the room. A new apartment appears on its definition when you double-click on a room in the corresponding dialog box, and you can assign a room to that apartment. Also, the newly created apartment becomes the current apartment, so newly built rooms are automatically assigned to it.
4. Resizing the image using the Paint editor.
5. Image resizing using MS Word.
6. Image resizing using Adobe Photoshop graphics editor.
7. Image resizing using the Corel Draw graphics editor.
8. List of used literature.
1. Introduction.
You can plan and visualize houses with almost any number of floors. Basically, only the amount of space available on your computer will affect the number of floors you can use - usually this will be enough. In order not to lose the track, in the development mode you can only record in one - the current floor. You can always switch between certain floors, but the entries are always relative to the current floor. They may be individual projectiles or also a set of projectiles.
The building is a collection of superimposed floors. Multiple buildings can be placed next to each other, allowing you to define different floor heights as well as different ground levels for different buildings. So it is quite possible to put a chair in a closet, which, of course, seems doubtful. To prevent this, you can use the so-called collision. This method calculates internally when moving objects and groups of objects whether they will collide with any other objects already placed.
This essay provides general information about
computer graphics, theoretical and practice-oriented materials on
the study of graphic computer programs such as Paint, MS Word, Adobe Photoshop and Corel Draw. The material contains text and graphic illustrations explaining the work of resizing graphic images.
Because collision control requires relatively a large number calculation time, and it would be tedious to move a cabinet from one room to another by pushing it through a door, collision control is usually not enabled. This will mean: if you get too close to the armchair closet, further movement in that direction is prevented. B. in assembling a cabinet wall from several individual cabinet parts is very useful. Part of the closet is now as close to the wall as possible. Now do the same with the second part of the cabinet as you did with the first.
computer graphics in recent times many are involved, due to
high rates of development of computer technology. Over 90% of the information is healthy
a person receives through vision or associates with geometric spatial
representations. Computer graphics has great potential to facilitate
However, push that part of the cabinet against the other until it is pressed further. Hull parts are now next to each other. However, it may be necessary to move the last part of the cabinet slightly closer to the wall. Both parts of the cabinet are now directly next to each other and as close to the wall as possible.
You can compare this procedure with the furniture in the room. The main difference, however, is that you can look at the result of returning the furniture - without special efforts- once per screen. If you are developing an application for small screens, tablet users will find your work unreadable and won't use it at all.
process of cognition and creativity, it allows students to develop spatial
imagination, practical understanding, artistic taste.
Main goals this abstract are acquaintance with the theoretical foundations of computer graphics and teaching the simplest methods of correction and optimization of graphic images for visual and didactic materials used in educational activities based on raster and vector graphics.
This tool is called the layout editor. Usually this is a file. Once opened, you should have something similar to the following picture. This tool allows you to set up views directly in the application's layout, represented by the middle window. This is the central window that contains the canvas and displays the specific result of our GUI. In this window, we will add, remove or modify components to integrate into our GUI.
This window contains a toolbar. This menu contains seven buttons that allow you to do three things. Change the window view preview to see what the GUI will give on a different type of terminal. Add resources to handle different situations, such as terminal management in landscape mode or to control other languages. Change GUI base. . Let's take a closer look at what these buttons are for.
2. Types of graphic editors.
used for image processing on a computer. special programs- graphic editor. A graphic editor is a program for creating, editing and viewing graphic images.
Consider some of the graphic editors:
1) Graphic editor Paint is a simple one-window graphic editor that allows you to create and edit fairly complex drawings. The Paint editor window has standard view. (fig.1)
There is also a toolbar. This panel is used to change the preview display. Nothing, nothing will replace the test on a real terminal. Don't think that because your GUI is aesthetic in this tool, it will be so in real life. If you don't have a terminal, the emulator will give you best review situations.
For example, it allows you to change view attributes on the fly. If you click on it right click mice, you can see various options available to you as shown in the following figure. 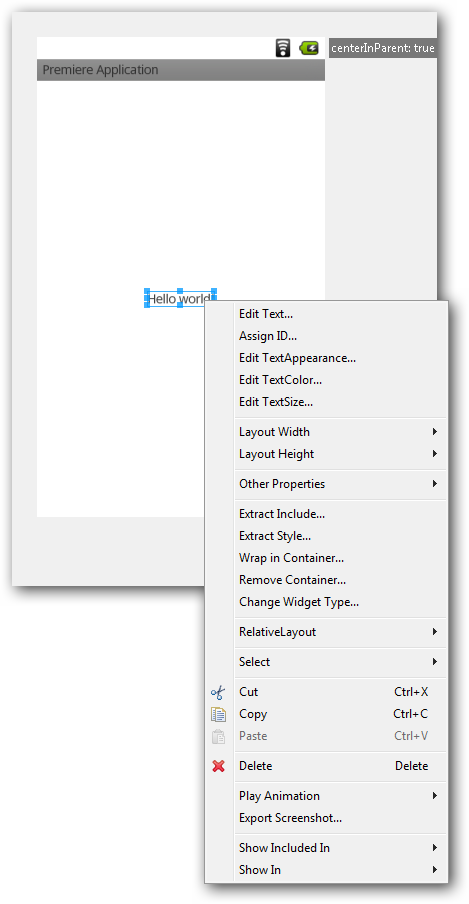
You will understand the meaning of these terms later, but remember that you can change attributes with a right click. You can also use the Properties tab at the bottom right.
2) Photoshop by Adobe is a multi-window graphics editor that allows you to create and edit complex drawings, as well as process graphic images(photos). Contains many filters for photo processing (changing brightness, contrast, etc.).
3) The program Microsoft Draw - included in the MS Office. This program is used to create various drawings, diagrams. Usually called from MS Word.
Also, you can post different types by clicking on them in the left menu and then placing them in an action as shown in the following image. 
You can then enlarge, reduce or move them according to your needs, as shown in the following figure.
Differentiation between layout and widgets

Let's return to the first view, which covers the other. Layouts simply arrange views in a certain way, and a view that cannot span others is called a widget. Of course, you can have a simple widget at the root if you want your layout to consist of this unique widget.
4) Adobe Illustrator, Corel Draw - programs used in publishing, allows you to create complex vector images.
Images in graphic editors are stored differently.
A bitmap is stored using dots various colors(pixels) that form rows and columns. Any pixel has a fixed position and color. Storing each pixel requires a certain number of bits of information, which depends on the number of colors in the image.
These two attributes can take one of the following three values. For example, if your view is displaying an image, it will barely take the size of the image, if it is displaying text, it will just take the size to write the text, an exact numeric value with a unit. It's exactly the same, but more explicit.
It's because we don't tell you everything, we hide things from you, but in a different place. In fact, even our root has a parent view, we just don't have access to it. This invisible parent view takes up all the space on the screen.
Vector images are formed from objects (point, line, circle, etc.), which are stored in the computer's memory in the form of graphic primitives and describe them mathematical formulas.
For example, a graphic primitive point is specified by its coordinates (X, Y), a line - by the coordinates of the beginning (XI, Y1) and end (X2, Y2), a circle - by the coordinates of the center (X, Y) and a radius (R), a rectangle - by the size of the sides and the coordinates of the upper left corner (XI, Y1) and the lower right corner (X2, Y2), etc. A color is also assigned to each primitive.
As a consequence, graphic editors fall into two categories: raster and vector. They differ in the way they present graphical information.
Definition and restoration of views
You can also define an internal margin for each widget, which is the spacing between the view's outline and its contents. 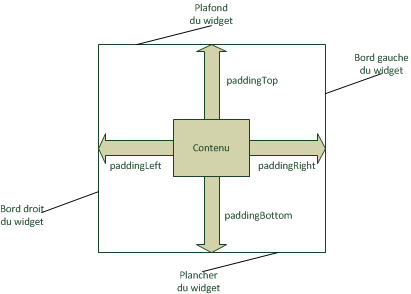
Well, that's simply because we have to create that ID ourselves. This means that we are talking about an identifier that has not yet been defined. Finally, we can use this identifier in code like other identifiers. Be careful, this method returns a view, so you need to cast it on the destination type. I don't know what that means!
Vector graphic editors.
Vector graphics are the best medium for storing high-precision graphic objects(drawings, diagrams, etc.), for which the presence of clear and distinct contours matters. With vector graphics you encounter when working with computer-aided design and computer-aided design systems, with processing programs 3D graphics. All components of a vector image are described mathematically, which means they are absolutely accurate. Vector images, as a rule, are built manually, but in some cases they can also be obtained from raster using tracing programs. Vector images are not able to provide realism close to the original, but the advantage of vector graphics is that the files that store vector graphics are relatively small. It is also important that vector graphics can be enlarged or reduced without loss of quality.
Try to do it earlier, your application will crash. What are you, right? When you deserialize a layout in an activity, you should get the widgets and layouts that you want to add functionality to. Very glad to see that you like our courses, already read 5 pages!
You will also be able to track your progress in class, complete exercises, and interact with other participants. The program is localized into several world languages, but we are nowhere in between. At the top you will find a menu bar and a toolbar for switching between modules, automatic editing, job selection, alignment, etc. tools for detailed image editing can be found in the vertical panel on the left side of the window.
Raster graphic editors.
Raster graphic editors are the best means of processing photographs and drawings, since raster images provide high precision transfer of gradations of colors and halftones. Presentation method bitmaps completely different from vector. Raster images are made up of individual dots called a raster. This representation of images exists not only in digital form. Raster images provide maximum realism, since every smallest fragment of the original is digitized. Such images are saved in much larger files than vector ones, since they store information about each pixel of the image. Thus, the quality of bitmap images depends on their size (number of pixels horizontally and vertically) and the number of colors that the pixels can take on. As a consequence of the fact that they are made up of pixels fixed size, free scaling without loss of quality is not applicable to them. This feature, as well as the very structure of raster images, somewhat complicates their editing and processing.
The parameters of the selected tool can be changed in the context panel. With right side the windows are side panels. You can move the sniper, connect them to strikes, snap them to the left side of the window, or let them float in the space above the image.
The program consists of five modules suitable for various kinds activities. We can switch between modules using the help keys on top panel. The other three modules already have a very specific focus. Press the button on the top bar to switch to "Character Development". On the right sidebar, go to the "General" tab and edit "Exposure" in the "Exposure" window.
But in addition to creating images, graphic editors allow you to store the resulting images. To do this, there are files that are different for vector and raster graphics editors.
3. Basic functions of the graphic editor.
Working in a graphics editor refers to graphics processing technology. Some generalized graphics editor is characterized by the following functions:
In the "Improve" section, we can quickly edit. the contrast or saturation of a photo. The tuna curve is used to handle tons in the most efficient way. We'll display it in the Tones box by selecting Curves. Once the execution is done, click the "Create" button in the pop-up panel.
Move and change the displayed mouse
Before moving, the View tool is located on the panel to the left of the window. If we are working with another tool, and if we don't want to stop it, we can trigger a transition to a temporary call by crossing the interline. To return to the original viewport where the window space is being filled, we quickly double-click on the Tool icon.
1. Create a drawing
a) In manual drawing mode;
b) Using the toolbar (stamps, primitives).
2. Pattern Manipulation
a) Selection of fragments of the picture;
b) Elaboration of small details of the picture (enlargement of fragments of the picture);
c) Copying a fragment of the picture to a new location on the screen (as well as
We will now focus on the Layers panel for working with layers. In the panel, click the "Correction" button. We choose a wide selection of cats. the first version of the Levels and the riding of the riders determine white dot and the value of Gamma. We will change the distortion of the ton in the picture.
Press the "Delete" button to clear the window and close the window by clicking the "Reset" button during the undo, but the "Levels" window remains open and we can try different settings, the Merge button confirms it and switches directly to the current pixels of the layer - so we don't need to confirm the so-called destructive call, but we don't even need to confirm - by changing the values directly with racers, we just close the window. In the Layers panel we will see new layer"Regulations".
the ability to cut, glue, delete image fragments);
d) Shading of individual parts of the picture with an even layer or pattern, the ability to use arbitrary “paints”, “brushes” and “spraying” for drawing.
e) Image scaling;
f) Moving the image;
g) Image rotation;
3. Enter text into the image
The layer level does not refer to pixels - it only contains information about what can be applied to lower levels. Removing the layers will cancel the treatment and this type of treatment is called non-destructive. In the Layers panel, we can do a few things with the rash layer.
The so-called filters are very similar. We place text as a workload with vector layer. On the toolbar, click the Artistic Text Tool button. AT context panel we measure its size, font, color, and ultimately the color of the outline.
Click on the picture and enter text. To move it, use the Move tool. In the Layers panel, we see the text as a new layer. Your best bet is to use the History panel to bring back more steps. Here is a list of steps taken from top to bottom. By clicking on a certain step, we will get the status after it is completed.
a) Font selection;
b) Selection of characters (italics, underlining, shading);
4. Working with flowers
a) Creating your own color palette;
b) Creating your own pattern (stamp) for painting;
5. Working with external devices(disks, printer, scanner, etc.)
a) Writing a picture to a disk (floppy disk) as a file of a standard format (pcx, bmp, tif, gif, jpg, png, etc.);
b) Reading a file from a disk (floppy disk);
c) Printing a drawing;
d) Scanning the drawing.
The mouse is most often used as a "brush", less often the cursor is used when controlling the keyboard. The toolbar is used to draw straight and curved lines, circles (ovals, ellipses), rectangles (squares).
4. Resizing the image using the Paint editor.
You can change the size or resolution of a digital image by changing the following characteristics:
The number of pixels. The resolution or sharpness of an image is determined by the number of pixels that make it up. Increasing the number of pixels improves image resolution. This allows you to print images big size while maintaining quality. However, keep in mind that the more pixels an image contains, the more disk space it takes up.
File size Volume disk space occupied by the image on the computer and how long it takes to send the image to e-mail determined by the size of the image file. Although increasing the number of pixels often increases the file size, the file type of an image (such as JPEG or TIFF) has a greater effect on the file size. For example, an image saved in TIFF format will be significantly larger than the same image saved in JPEG format. This is because the JPEG image can be compressed. This reduces the file size at the cost of slightly degrading image quality.
Presentation of data on a computer monitor graphical form was first implemented in the mid-1950s for mainframe computers used in scientific and military research. Since then graphic way data display has become an integral part of the overwhelming number computer systems especially personal ones.
Computer graphics is a special area of computer science that studies the methods and means of creating and processing images using software and hardware computing systems. It covers all types and forms of representation of images available for human perception either on a monitor screen or as a copy on external media(paper, film, fabric, etc.).
Without computer graphics, it is impossible to imagine not only a computer, but also an ordinary, completely material world. Today, computers and computer graphics are an integral part of life. modern society. Let's take medicine as an example CT scan), Scientific research(visualization of the structure of matter, vector fields and other data), modeling of fabrics and clothing, experimental design, billboards, color magazines, special effects in films - all this is to some extent related to computer graphics. Therefore, programs have been created for creating and editing images, that is, graphic editors. In my examination paper, I most fully disclosed the issue of graphic editors in order to further apply the acquired knowledge in practice, that is, when making a presentation on the topic “This is our class”.
> Main body
> Types of graphic editors
To process images on a computer, special programs are used - graphic editors. A graphic editor is a program for creating, editing and viewing graphic images.
Consider some of the graphic editors:
Graphic editor Paint is a simple one-window graphics editor that allows you to create and edit fairly complex drawings. The Paint editor window has a standard view. (fig.1)
Photoshop by Adobe is a multi-window graphics editor that allows you to create and edit complex drawings, as well as process graphic images (photos). Contains many filters for photo processing (changing brightness, contrast, etc.).
3) Microsoft Draw is included with MS Office. This program is used to create various drawings, diagrams. Usually called from MS Word.
4) Adobe Illustrator, Corel Draw - programs used in publishing, allows you to create complex vector images.
Images in graphic editors are stored differently.
A bitmap image is stored using dots of different colors (pixels) that form rows and columns. Any pixel has a fixed position and color. Storing each pixel requires a certain number of bits of information, which depends on the number of colors in the image.
Vector images are formed from objects (point, line, circle, etc.), which are stored in the computer's memory in the form of graphic primitives and mathematical formulas that describe them.
For example, a graphic primitive point is specified by its coordinates (X, Y), a line - by the coordinates of the beginning (XI, Y1) and end (X2, Y2), a circle - by the coordinates of the center (X, Y) and a radius (R), a rectangle - by the size of the sides and coordinates of the left upper corner(XI, Y1) and the lower right corner (X2, Y2), etc. A color is also assigned to each primitive.
As a consequence, graphic editors fall into two categories: raster and vector. They differ in the way they present graphical information.
Vector graphics editors
Vector graphic images are the best medium for storing high-precision graphic objects (drawings, diagrams, etc.), for which the presence of clear and distinct contours is important. You encounter vector graphics when working with systems computer drawing and computer-aided design, with programs for processing three-dimensional graphics. All components of a vector image are described mathematically, which means they are absolutely accurate. Vector images are usually built by hand, but in some cases they can also be obtained from raster images using tracing programs. Vector images are not able to provide realism close to the original, but the advantage of vector graphics is that the files that store vector graphics are relatively small. It is also important that vector graphics can be enlarged or reduced without loss of quality.
Raster graphics editors
Raster graphics editors are best remedy processing photographs and drawings, since raster images provide high fidelity in the reproduction of gradations of colors and halftones. The way raster images are represented is completely different from vector images. Raster images are made up of individual dots called a raster. This representation of images exists not only in digital form. Raster images provide maximum realism, since every smallest fragment of the original is digitized. Such images are saved in much larger files than vector ones, since they store information about each pixel of the image. Thus, the quality of bitmap images depends on their size (number of pixels horizontally and vertically) and the number of colors that the pixels can take on. As a consequence of the fact that they are composed of fixed size pixels, free scaling without loss of quality is not applicable to them. This feature, as well as the very structure of raster images, somewhat complicates their editing and processing.
But in addition to creating images, graphic editors allow you to store the resulting images. To do this, there are files that are different for vector and raster graphics editors.