Victoria hard drive repair. How to recover bad sectors on a hard drive using Victoria? Checking the hard drive for bad sectors
Victoria is a PC program aimed at a wide range of users. Used to recover information from hard drives with SATA and IDE interfaces for testing them. The program allows you to deeply, from all sides and quickly assess the condition of your hard drive.
Key Features
- – shows full technical information about the hard drive
- – Manipulation with the level of sound noise
- – restoration and change of the physical volume of the drive
- – you can view s.m.a.r.t. settings, instant assessment of the state by the status register and pseudographic scales.
- -full and evaluation modes of surface plotting
- - is able to determine the controllers available in the SATA / ATA system, as well as additional
- – method of redistribution of sectors from the reserve hides surface defects
- - measurement and control of hard drive performance
- -tests the interface and buffer memory, during the reception and transmission of information, for the presence of bugs and data distortion
- – it is possible to start and stop the drive spindle motor
- - cleaning the entire hard drive or part of it
- - allows you to adjust the speed of reading by graphic methods
- – allows you to measure random, linear, non-linear read speed from a disk.
- - you can measure the rotational speed of the shaft
- – copying data by sectors of the hard disk
- - indication of hard drive operating modes, visualization of error codes through indicator lamps
victoria how to use?
Download the program from the link. We unpack and rewrite the disk image with the .iso extension available there to disk. It is important not only to burn this file to disk, but to burn the image itself.
Next, you need to run the program. This is done using the BIOS. We insert our disk and turn off the computer. To get into this BIOS, you need to press DEL or F2 on the keyboard when you turn on the computer. When you get to the blue BIOS menu, do the following.
We select "Advanced Features", in it "Boot sequence" and you need to select boot from CD / DVD. Then you need to save everything and exit by clicking "Save and exit setup". If your BIOS menu does not have such items, then look for something similar with the word boot.
If everything done is correct, you will automatically leave the BIOS and Victoria will start

Launching "Victoria" and data recovery
When you run the program for the first time, you will need to press "P" on the keyboard to select the drive you need. In all menus, the desired item is selected using the "down" and "up" keys. When moving the cursor, an indication will be noticeable, which means that the hard disk is ready.

For drives that are working normally, two indicators DRDY and DRSC are lit, INX may be lit.
The AMNF indicator may be lit in the error register. The rest should be inactive.
Now we select the item we need with the enter button and the program looks for external controllers and hard drives on them. After that, all serviceable and really present HDDs in the “master” position will be determined. The rest of the drives will not be noticed. Then, after finding additional ports on the screen, information will appear in the form of a table.
It contains the name of the controller developer (Vendor code), the name of the controller itself (ID Code), class (EXT, INT, RAID), port address (if not found, then a dash), HDD name (only if it is working ). In the plate, everything will be numbered in order and you will need to select the one you need.
It is also possible that Victoria will not find drives on all Promise controllers. And therefore, click on F2, thereby opening the passport of our drive. The passport itself contains data on the characteristics of the HDD and describes its parameters. When analyzing a disk, the program takes into account the data in the passport.

Hard drive testing
Victoria has a good hard drive surface scanner. It allows you to diagnose the hard drive for the presence of failures, interface errors and floating defects. The program can test most drives at maximum speed. And it does not depend on the type of interface cable and controller.
Unlike other utilities of this type, exclusive algorithms are used here. They include adjusting the timer depending on the speed of the hard drive. Supported standards are recognized automatically. Thanks to this, you can test both fast and slow HDDs. Its original way of measuring time intervals makes it possible to work with the program through virtual DOS on Windows and almost does not reduce accuracy.
The surface test is closely related to the drive passport. LBA 28 and 48 bit modes are supported and automatically recognized. Everything that could be done automatically was done and no settings are required from the user.
Linear Reading (Verification)
Carries out a surface test in LBA addressing. Made for fast and accurate diagnosis of surface conditions. During the test, the program divides the entire HDD address space into conditional identical sections. The access time to each site is measured and a rectangle of the corresponding color is drawn on the screen.
Random reading
Surface test in which a random number generator is involved. This generator gives the addresses of the sides. The range is set in the test menu. The result obtained by the test quite accurately describes the speed of the drive in real tasks.
Butterfly reading
The butterfly algorithm alternately reads the end and the beginning of disk space, shifted by one block. It differs from random in that this test scans the entire surface and all sectors according to a certain law and has an end. Performs a much slower scan than a linear scan.
PIO reading
In this case, there is a real reading of sectors from the hard drive. The speed is low - 2-8 megabytes per second. Therefore, such reading is best done in small areas. Effective for detecting drive bugs and checking the operation of the interface and the read channel. To increase the read speed, you need to enable the maximum mode (PIO-4) in the BIOS.
PIO read to file (Read to file)
What distinguishes this method of reading "not to a file" is that information from the HDD is written in the current directory to a file. Victoria handles bad blocks in such a way that zeros are put in place of defective sections. On error, the sector is read twice. First, with block access, then with sector-by-sector access.
Write(Erase)
Sector data is being erased. Used to remove some defects. Erasing speed is close to PIO reading. But there is a faster way to delete information through the security subsystem.
Write from file
The contents of the file are written to disk by sectors. Through the built-in manager, a window will open where you can select a file. The speed of such recording reaches six Mb / s. The procedure takes place with the participation of a visual scanner. Useful for cloning small drives and fixing file system corruptions. The maximum file size is 2GB.
In order to test the surface of the hard drive, use the F4 key. You will see a menu. In it, select "Linear reading" and below "Ignore bad blocks" (ignore bad sectors). We select the space button, navigation with the arrow keys - "up" and "down".

It is worth paying special attention to the third point. It has such functions as: writing from a file and writing (erasing). When they are used, data from the drive is erased. You can also lose data using "BB = Erase 256 sect". It's in the fourth menu.
After selecting the actions we need, scanning starts. The results will appear after a while in a special window.

There may be problems during the scanning process. The hard drive freezes due to a system malfunction. If the diagnostic test hangs, the program continues after a timeout of 16 seconds. To indicate the timeout, Victoria shows the symbol "T" on the display. Frequent freezing of the program may mean that the HDD is not responding to requests. You can solve this problem by pressing F3 (Reset). If something is not clear, then use the help system (F1 key).
Checking the program interface
In order to do this, press F4 on the third menu item. There is a record of cycles of information in the memory buffer of the hard drive, and then reads it from there. Comparison of the read data with the written ones is also performed. Reading time is also measured. If what is read does not match what was written, the program reports this. To get a complete picture of the state of the hard drive, you need to diagnose it for quite some time.
To exit the program, click on "X". After you exit, you will find yourself in "Volcov Commander". The exit from which is carried out by pressing F10 and confirming yes. Next is the "DOS" section. Ctrl+alt+del exit. The PC reboots and you need to remember to remove the disk from the drive and choose to boot from the hard disk.
Symbols for indicators
- DriveReady (DRDY)- the hard drive is ready to work and receive commands
- DriveSeek(DRSC) – the past value of the fact that the HDD has finished installing the head on the track is outdated.
- Busy (BUSY)– the drive is busy processing data or “freezes”. As long as this indicator is on, everything else does not work and Victoria only reacts to reset (F3).
- Index(INX)- this indicator appears after each turn of the hard drive. Not used on all devices.
- eror(ERR)- means that an error has occurred. By its code, you can find out what it is by register.
- data request(DRQ) – the hard disk is ready to start the process of information exchange with the interface.
Error codes
- UncorrectableDataerror(UNC)– information is not corrected by redundant code, recognized as unreadable. The error may be due to damage to the hard drive or a violation of the data checksum.
- IDNotFound (IDNF) – Sector not found. Basically, this means that the microcode or the lower level format of the drive is corrupted. Such an error appears for those who work properly, if you access an address that does not exist.
- Aborted Command (ABRT) – the hard disk failed to execute the command due to a malfunction or the command cannot be executed because not supported by the drive.
- AddressMarkNotFound (AMNF) – means that the sector cannot be read. Most likely it is a consequence of a hardware problem.
- Track 0 Not Found (T0 NF) – fails due to the inability to recalibrate the starting cylinder. If you have a modern hard drive, then such an error may indicate the inoperability of magnetic heads or microcode.
Above, information was provided on how to use the victoria program. This program is free, which is a big advantage. Also, it does not require installation, takes up very little memory, and works quickly. It includes many modes and thus surpasses similar programs (Dalas, hddl, veryfi, vivard, etc.) with all of the above.
Victoria hard drive surface check
Recovering deleted files is not a problem, there are dozens of utilities for this. But what if the drive is corrupted, has a bad geometry definition, or is password-protected at the controller level? Then the Victoria utility comes to the rescue. It is written in assembler, takes a few kilobytes and works directly with the controller.
WARNING
All information is provided for reference. Victoria uses low-level operations, the meaning of which is described in the manual. The editors and the author are not responsible for any possible harm.From MS-DOS to Windows 10
Victoria was conceived as a tool for advanced diagnostics of drives (then - hard drives, and today also SSDs) and managing their settings through low-level commands. Belarusian programmer Sergei Kazansky has been developing it for ten years and has released an author's set of utilities for data recovery. During this time, there have been many commercial releases of Victoria, several free versions and one unofficial one, which we will pay special attention to.
Victoria was originally a disk utility for MS-DOS written in assembler. The ancient operating system was better suited than Windows, due to the fact that in a single-tasking environment it is easier to provide exclusive access to the disk. With the advent of support for the porttalk.sys driver, Victoria versions 4.xx learned to work in the WinPE multitasking environment, as well as in Windows from XP to 10 of any bitness. It has become easier to run it, the actions in the graphical interface have become clearer, and the mode of operation itself has changed. But here's the problem: without understanding the new features of the program, some users began to lose data and entire disks instead of restoring them. Therefore, the latest official version 4.46b has a developed "fool protection".
By default, only non-destructive operations with drives are available in it. This is not just a read-only mode, as in other utilities that access the HDD / SSD using the Windows driver. Victoria also blocks the ability to change HPA (and mess with disk geometry), accidentally start low-level formatting and “shoot yourself in the foot” in more sophisticated ways at the first start.
Universal Soldier
Victoria is the most versatile utility. It accesses any type of storage device (HDD, SSD, USB Flash) and with any ATA-compatible interface. Its job is to send ATA commands to any device that supports them. Therefore, everything that has been said about Victoria's work with disk drives is also true for solid-state drives, with the exception of what applies to their design features. It is clear that it is pointless for an SSD to watch the spin-up time of the spindle and try to control the positioning speed of the heads - it does not have either. Nevertheless, it is quite possible to test and even restore an SSD using Victoria.
Victoria 4.47
This version was made in 2013 by Oleg Shcherbakov, a programmer from Moscow. He patched the latest official build of Victoria 4.46b. Download is better. On this site, Shcherbakov published it along with the patch sources. The rest of the resources can distribute anything under the guise of the new Victoria.
INFO
At the time of writing, the abandoned site of the developer of the Victoria program was infected. Therefore, instead of the URL www.hdd-911.ru specified in the documentation for the program, a link to an alternative source for downloading the Victoria utility is provided.Although Victoria is far from a new program, there were also critical errors in it that needed to be corrected. One of them led to the fact that it was impossible to run Victoria on 64-bit versions of Windows. Because of the other, problems could arise when working with large disks. If the volume was higher than a terabyte, then Victoria 4.46b simply spent all the virtual memory on rendering and color marking the checked LBA blocks. In version 4.47, Shcherbakov fixed all this.

PIO vs API
Victoria has two modes of operation: PIO (port input/output) and API (application programming interface). In PIO mode, the drive controller is polled by the program through the porttalk.sys driver. If you select API, the operating system tools will be used. Disk performance in PIO mode drops because DMA and high-level read and write optimizations are not supported. However, PIO mode allows you to use all the features of Victoria and send any ATA commands directly to the disk controller, bypassing the OS and standard drivers. It is through PIO that they most often work with disks in data recovery laboratories. Victoria supports both drives with a modern SATA interface, as well as old ones - PATA (aka IDE). Victoria can also work with external drives (features will be described below).
Having selected the PIO mode, at the beginning of work, you need to scan the bus and determine the disk controllers with the PCI-Scan button. To the right of it, a disk port selection window is displayed. Internal drives are usually detected without problems, but for external drives, you will first have to find out their port. This can be done in the hardware properties or in any diagnostic program (for example, AIDA64). After that, you must manually set the port in Victoria. Even when scanning, you can check the All dev checkbox (all devices) and use the exclusion method to find the desired disk in the list of found ones.

It is advisable to use the PIO mode for low-level commands. A simple search for bad sectors and their reassignment to a spare disk area is much faster (but less reliable) in API mode.
The limitations of the API mode are as follows: you cannot set or remove ATA passwords, work with the Host Protected Area and view registers are also disabled. If any of these functions are needed, then you can switch to PIO mode. It happens that the PIO mode is not available. This happens when using older versions of Victoria on 64-bit OSes. Another reason may be errors in working with the porttalk.sys driver or the choice of SATA AHCI mode. You can definitely get out of the situation in the following way.
- We write down the boot
with WinPE x86 and put the Victoria program on it by simple copying. - We connect the required drive to the SATA / PATA port, if we have not already done so.
- Disable all other HDD or SSD (optional).
- We go into the CMOS setup, switch the SATA controller mode from AHCI to compatible (compatible, native or IDE).
- Download WinPE. If necessary, install additional drivers, including porttalk.
- We start Victoria in PIO mode, initialize the required HDD or SSD and execute the necessary command.
Settings can be set through the GUI or in the vcr40.ini file. The same file will help to remove the blocking of work with the primary port. It is enabled by default to protect the system disk from accidental modification. To be able to select Primary from the list of ports, you need to do two things:
- Disable the "only non-destructive functions" option and close the program.
- In the section of the vcr40.ini file, add the line Enable PM=1 , save the changes and restart the program.
porttalk
The latest versions of Victoria are able to automatically install the porttalk driver, but it is completely useless on 64-bit systems. The fact is that, for the sake of greater security, they removed a couple of functions that are needed for porttalk and Victoria to work. Therefore, the porttalk driver (and, accordingly, the PIO mode) only works in 32-bit versions of Windows, where there are Ke386SetIoAccessMap and Ke386IoSetAccessProcess functions.
External drives
External drives are ordinary laptop (2.5″) or desktop (3.5″) models in containers with USB and FireWire interfaces. They are supplied with various controllers with the general name "SATA bridge". Many of these bridges do not translate low-level commands. Therefore, with some external drives, Victoria can immediately work in PIO mode in the same way as with internal drives, while with others you will first have to suffer. In the simplest case, it will be enough to remove the disk itself from the case (do not open the HDA!) and connect it directly to the port.
Rare beast: SATA hard drive without SATA port
At Western Digital and, possibly, other manufacturers, some external hard drives were already produced with a soldered SATA - USB bridge. Therefore, they do not have a conventional SATA connector. Nevertheless, they can still be connected directly to the port by soldering the SATA cable to the pins on the drive board. To understand if your drive belongs to such a series, you will have to google by model number and look for datasheets.
Passwords
One of the most requested low-level commands in PIO mode is working with passwords. According to the specifications, access to the disk can be restricted with a password. It is set by the user from the BIOS or using external utilities. There is also a factory-preset master password. You can only lock a drive with a custom password. If you forget it, then the lock can be removed with a master password.
Depending on the set security level, the result of entering the master password will be different. At a high level (high), the master password acts on a par with the user password. It just unlocks the drive and that's it. If the maximum security level (max) is set, then entering a master password instead of a user password will unlock the disk only after all data on it has been completely erased (secure erase).
Working with ATA passwords is further complicated by the fact that, according to the standard, they always consist of 32 bytes (no matter how long you set it). Extra characters are ignored, and the missing ones are added automatically. The problem is that different programs write them in different ways. Regular security utilities on some laptops are especially guilty of this. Instead of traditional zeros (or at least spaces), they use non-printable characters. The code 00h cannot be typed at all from the keyboard (even through (ALT) + code). There is only one way out: do not enter the password in the program window, but read it from a file. Any characters can be written to a file using a hex editor.
It is not uncommon for a user to be unable to unlock a drive even when they enter the correct password. When changing a laptop or losing a regular utility, any other utility (for example, HDDL) will append the password to 32 bytes with its own characters.
There is also a preliminary modification of the password. In many laptops, it is actually encrypted before being sent to the controller. Usually these are the simplest logical operations, but this does not make it easier. The user thinks that there is a password known to him, while in reality the controller accepts a completely different one. If you have tried all the variants of the supposed user and standard master passwords, but have not achieved a result, then there is only one way out - to carry the drive to the laboratory, where they will work with it in the technological mode.
How to get back a lost terabyte
Sometimes it helps a lot to work Victoria in PIO mode with HPA (Host Protected Area) - a service area of memory in which the disk geometry is recorded. It determines the capacity of the drive by specifying it as the number of LBAs.
In my practice there was an amusing case. Received the standard complaint: "the computer does not turn on" (read, the OS does not boot). The owner complained that he had been suffering for about a month. First, he traveled to all the service centers, then he invited various enikey workers - to no avail. I came, looked and also thought hard. All components are correct. The disk is detected in the BIOS, but it does not boot from it. Launched Linux from a flash drive. The hard drive is visible, but the logical partitioning utilities show a strange picture: 64 MB in total and one partition with an unknown file system.
And then I realized that the HPA just crashed on the hard drive. As a result, a terabyte disk began to be defined as a 64-megabyte stub. I switched the SATA port mode from AHCI to compatible in CMOS setup, took a USB flash drive with WinPE and launched Victoria in PIO mode. Then he sent the NHPA command (restore factory volume).
Usually in such cases it is possible to instantly restore the passport value of LBA blocks, but this time the miracle did not happen. Therefore, I found a service utility for hard drives of this series and sent a similar HPA recovery command from it. A terabyte of data returned from oblivion on the next reboot.
Why did Victoria let her down? I suppose because this disk had some specific features unknown to me or the universal program.
Bad sectors
Most often, Victoria is used to find and fix bad sectors. If everything is in order with HPA on the disk and password protection is not worth it, but no utilities can read files from it in a reasonable time, then it's time to check the surfaces. Victoria can do this in any mode (PIO / API) using sector-by-sector reading (read), writing (write) and writing with verification (verify).

When restoring data, you can use read-only, but its options also vary. The simplest of them is sequential: from the first block to the last. The start and end values of LBA can be specified manually, which is convenient for many reasons at once. Firstly, this way it becomes possible to check disks of any size, simply by performing the test in fragments up to one terabyte. Secondly, you can re-check the suspicious area and exclude external factors. Victoria analyzes the sector access time. Usually, for new disks, it does not exceed 5 ms in 80% of sectors. Sectors with a polling time of less than 50 ms are also considered normal. Those for which it is measured in hundreds of milliseconds are candidates for bad sectors.

If the sector was considered after a few seconds, then this is an unambiguous bad block. Such a disk controller must identify itself during idle time and replace them in the address table with good sectors from the spare area. However, in practice this does not always happen. Victoria can ask the hard drive to perform such an operation (Remap) for those sectors that have not responded to requests for too long. Formally, part of the information is lost during this procedure, but in reality it was already lost at the moment when the sector became faulty.
In the paid version of Victoria, the Restore function was available - an attempt to read data from a bad sector at any cost and then overwrite it with a good sector. However, the program has not been officially supported since 2008, so it is unlikely that you will be able to purchase its full version. Free Victoria has more than once helped out by restoring HPA, resetting passwords and fixing bad sectors, which caused other data recovery programs to freeze.

How Free Victoria Saved a Secret Job
Let me share with you another story. Laboratory at the research institute, our time. The analytical instrument is controlled from the computer that came with it. A very specific software is preinstalled on the computer, which the developers no longer support. The distribution kit is neither on the disk nor on the site. There is only an installed program, and it stopped working. The laboratory performed research under a multi-year government contract. Without a miracle device, the employees were bound hand and foot. We tormented ourselves and found out that the problem was with the disk. From antiquity, it was covered with bads, and normal work became impossible. An attempt to make a clone of the disk with skipping bad sectors was unsuccessful - the cloning program hung tightly. We ran the disk with the Victoria test with the Remap function. Pre-selected the necessary settings. By the evening of the same day, they successfully removed the disk image, and then restored everything from it to a new hard drive. The device came to life, the contract was completed on time.
Additional features Victoria
Victoria analyzes the state of the drive in detail and can fix almost any failure in its operation. Actually, this Victoria differs from the mass of other utilities. If most programs simply show SMART attributes, then it can force entire sets of self-diagnosis tests to run.

Victoria has four methods and three types of surface testing (twelve modes in total). In each, it automatically counts the total number of defective blocks and writes their addresses to the log. Like a disk editor, Victoria can show the contents of sectors and allows you to change it. In PIO mode, Victoria displays information about the logical partitions on the media, even if it is not detected at all in the BIOS. Not a single utility with access through the API is capable of this. Additionally, Victoria can control the level of acoustic noise of the disk (AAM), adjusting the speed of movement of its heads during the search, run low-level formatting, change the HDD volume and perform benchmarks. It can even be used to check the physical interface (cable and port status). At home, it will save the HDD or SSD in many difficult situations, except for severe mechanical damage that requires opening the HDA. The lab will handle them too, using Victoria as one of the proven utilities.

Conclusion
Much more can be written about Victoria, but for details I still have to send you to the Russian-language documentation. And, since the versions of the program differ in all sorts of subtleties, I recommend reading the manuals for versions 3.5.2, as well as 4.46b and 4.47.
“Find the beginning of everything, and you will understand much.”
/Kozma Prutkov/
The interface of the Victoria program is a Windows window - the main form, which contains:
- 5 sheet tabs.
- Common for all tabs:
- Top menu with buttons and indicators.
- Sidebar with buttons and indicators.
- Text log 4
Let's take a look at all the elements of the Standard tab one by one.
1
— Switch of access modes to the drive under test. It has 2 positions - API and PIO.
API is an abbreviation for "Application Programming Interface", and translates as "Application Programming Interface". This means that the program uses the built-in Windows access to the tested drive for its work, in particular, system drivers.
PIO is an abbreviation for "Programmed input/output", and translates as "Programmed input/output". Means the mode of access to the tested drive directly through the input / output ports, bypassing the Windows functions, BIOS and drivers. In this chapter, we will consider only the API mode, as the most simple and universal.
In some cases, the API/PIO switch may be disabled (inactive) and forced into API mode. This occurs when PIO mode is not possible, such as on 64-bit operating systems.
2
- In the upper right corner there is a list of Windows drives found by the program at the time of launch or when API mode is enabled. The list is numbered, starting with the number 0. Each line indicates the size of the drive and its name as provided by its developer for Windows. Some lines may be empty:
- Disconnected drive - the device was disconnected while Windows was running (for example, a USB flash drive);
- Invalid geometry - the device, such as a DVD drive, does not contain media (no disc is inserted), or the drive is defective;
- Etc.
In addition to numbers, the list contains letters of logical drives of removable devices. This is done in order if some device is not displayed in the list under the number. Drive letters can be hidden by unchecking "Show logical drives" on the "Setup" tab, but more on that in the corresponding chapter.
It is important to know that the devices in the list are not displayed automatically! The list must be updated manually after connecting or disconnecting each drive.
It was made on purpose. After all, the program can be used to study a drive that is not quite serviceable, and extra calls are harmful to it.
To update the list of devices, click on its title.
In addition to displaying disks, a list 2
also serves for choice tested drive. To do this, just click on the desired line of the list. In this case, the passport of the drive is displayed on the left side of the form.
3
. So the device is selected. In most cases, this will be a hard drive - a disk drive with an ATA interface. The abbreviation ATA, "Advanced Technology Attachment" is a standard for working with hard drives, which includes a standard command system and standard data structures. That is why the first tab of "Victoria" is called "Standard". One of these standard structures is the so-called "drive passport".

The passport contains many technical parameters of the drive:
- Model- name of the model and manufacturer;
- Firmware— microcode (firmware) version of the device;
- Serial— serial number of the device;
- disk size- the size of the disk in logical sectors and the conversion of the number of sectors into units of volume;
- CHS- disk geometry (obsolete, but sometimes necessary parameter) - the number of cylinders, heads and sectors on the track;
- SMART— information about the S.M.A.R.T. self-diagnosis system;
- CACHE— information about the cache buffer of the drive. Look-Ahead - read prefetch. Write - write buffer. The cache is used to speed up data exchange operations between the computer and the disk.
- Support— supported functions of the drive: will be described later;
- AAM val is the current value of the acoustic noise control mode;
- APMval— the current value of the power saving mode;
- Erase- the time it takes the drive to completely destroy information by erasing the built-in security subsystem;
- security— Security subsystem and its state;
- ATA-8- Supported features of the extended ATA standard. Practically, ATA-8 is SATA.
- Sector— sizes of the logical and physical sectors of the drive;
In the process of improving the Victoria program, new and relevant parameters will be displayed in the passport, and obsolete ones will be deleted.
Under the passport there is a panel with buttons and indication:
6, 7
- Indicator LEDs showing the speed of rotation of the HDD disk or the presence of a semiconductor drive - SSD.
SATA dev- the device has a Serial ATA interface (although it can be a USB drive).
Removable- removable device (flash drive, DVD);
Virtual- Virtual disk, such as the BestCrypt container;
9
— Jackdaw Save bin. If it is installed, then the program saves the structure with the passport to the directory with logs, from where it can be extracted at any time and loaded into the program with the button open bin. In this way, you can look at the characteristics of a physically missing drive or send a passport file for research.
8
- It's just a button for obtaining a passport, duplicating a mouse click on the line of the list of disks. It is also associated with a function key F2
.
10
— A text field for entering a password related to managing the drive's security subsystem (“Security manager” group). However, to avoid problems, these controls are only unlocked for USB HDD/SSD drives and in PIO mode. Working with this subsystem will be discussed in a separate chapter. The text field can also be used for other purposes, such as entering any commands, keys for paid versions of the program, and so on.
4
- Text log (event log) of the program. Designed to display messages from the program to the user. Each newly printed line scrolls the log up. At the same time, all lines are written to a text file, the name of which can be specified on the Setup tab.
The contents of the entire log, individual lines or a numeric value - can be copied to the clipboard through a right-click. The log can be cleared with the button 18
. If the number of lines in the log exceeds 1000, then it is cleared automatically to save PC memory. In this case, all information remains in a text file.
When you press a key F7- the program shows the last 20 lines of the log in a separate window.
Consider the functions of the sidebar, common to all tabs.
11
- Sleep button - HDD sleep mode. Designed to stop the rotation of the engine on the HDD or put the SSD into sleep mode. This action makes sense primarily for USB devices, or those drives that are not accessed by system processes. Otherwise, with any attempt to "sleep" - the very first call of the system will bring them out of this state.
12
- Recall button. HDD recalibration. Designed to wake up the drive from sleep mode. The HDD spins the shaft and sets the heads to track 0.
13
— Indicator LED of the state of program transients. If it is off, then the program is running normally (or inactive, or a test is running). Yellow color - indicates the execution of preparatory operations (for example, lengthy calculations or waiting for an event). A green indicator means that a button has been pressed. 14
"Break All" - "break everything." This button causes the immediate termination of all actions that depend on the program itself. Her reaction is instant. However, it cannot interrupt the operating system's initiated access to the drive and processes within the drive's firmware. It is for this reason that professionals almost never work with disks through the API.
15
- Indicator LEDs showing what the program is currently doing with the drive: reading or writing data? When the program is reading, the green LED lights up. When recording (erasing, repair operations) - the red LED lights up. If an action is performed with the drive without data exchange (verification, erasure through the security subsystem), then the LEDs will still turn off.
16
- Power button. HDD power management through an external switch included in the data recovery equipment. This button is not functional in the free version of the program, and has a purely decorative function.
17
- Checkbox for turning off the sound in the program.
18
— Button for clearing the text log window.
19
as well as F8— Calling the HEX-viewer of program buffers. Allows you to "look" in real time inside the hard drive from which information is read.
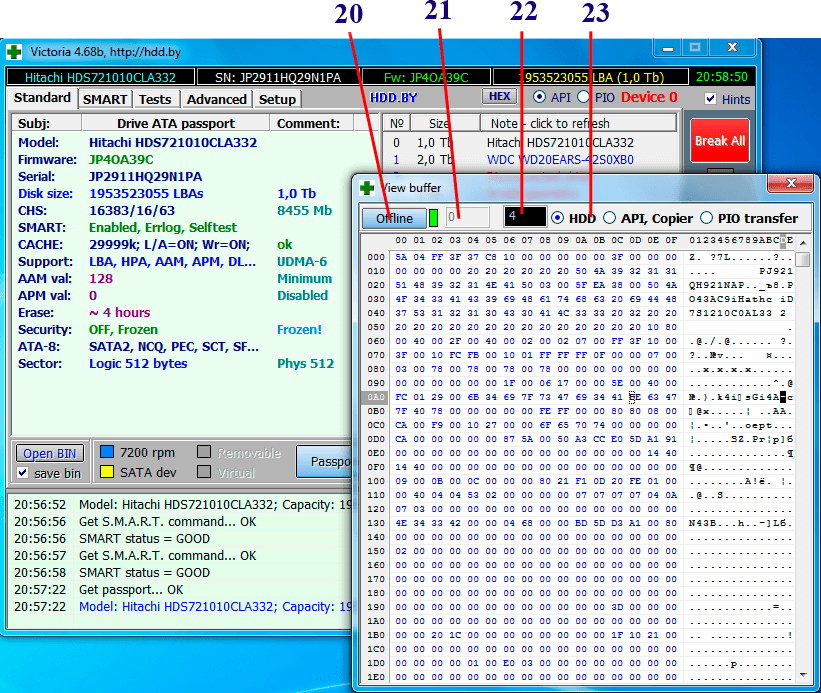
23 — Selecting the buffer to be viewed:
- HDD- a buffer into which the disk sends service data. We received a passport - there was a 512-byte passport structure in the buffer. We got SMART - we see the table of trashholds (it is taken last). We pressed the Recall button or launched a surface test - the contents of sector 0 were displayed in the buffer.
- API, Copier- read buffer from the drive. We launched a read surface test - and we can observe a continuous stream of readable data.
- PIO transfer- used to work in PIO, remap and auxiliary operations.
22
— The size of the selected buffer in sectors of 512 bytes. Static, displayed as reference information.
20
- Button to disconnect the viewer from the buffer. Offline mode allows you to take a look at content at a leisurely pace if it changes quickly.
21
— Data offset position in the buffer, active only in Offline mode. By scrolling this value with the mouse or entering a number manually, you can view different sections of the buffer. The change step is 512 bytes.
When you right-click on the passport field, a menu of additional actions appears.

- Copy ALL— Copy the text of the entire passport to the Windows clipboard.
- copy value— Copy the selected line of the passport to the clipboard.
- Get passport- Get a passport. Similar to the "Passport" button or key F2 .
- Maximize- Expand the field of the passport in width. At the same time, some of the interface elements are moved outside the form. You can also arbitrarily move the edge of the passport window with the mouse. The same action can be performed without the menu by double-clicking on the field.
- Big/Small- Seal the lines of the passport in height by reducing the distance between them.
To be continued…
Good day, dear readers, admirers and all other personalities! Today we will talk about diagnostics by the program. Victoria(below in the text we will simply call her Victoria or Vika :)). The whole process is divided into 2 parts and 4 stage, and in general, it is extremely simple, if you follow the instructions.
This diagnosis is needed in order to find and identify his current health.
Unlike the once mentioned utility Chkdsk(“How to Check a Disk for Errors” or “Chkdsk Utility”) described below Victoria, is a representative of a class of programs that work with the equipment under test directly through ports, that is, at the lowest level, which allows you to get the highest performance possible (that is, to achieve better, more extensive and intelligible diagnostics), although it complicates the process of creating and using such ON.
Here we go?
We will consider two options for working with the program:
- Part 1: version 3.35 from external media.
- Part 2: version 4.46 from under Windows.
Stage I: Installing and preparing to run Victoria from external media
First, download Victoria (here is the version 3.5 , which is best suited for out-of-system diagnostics).
After launching the program, you need to select our flash drive, specify the file system format and select the image we downloaded, approximately as indicated in the screenshot below:

Attention!
All data on the flash drive will be deleted after clicking on the " go", so it is recommended to first transfer everything from there.Do you want to know and be able to do more yourself?
We offer you training in the following areas: computers, programs, administration, servers, networks, site building, SEO and more. Find out the details now!
Next, we need to boot from the disk / flash drive where we recorded the image. To do this, insert the disk into the computer, reboot, go to (button DEL or F2 at the earliest stage of booting the computer) and there we set the boot from the disk in the manner described below (depending on how your BIOS).
Option 1. If your BIOS has the following form, then first go to advanced features


Where to put in the first place the download from CD/DVD drive just like in the picture.
Then exit from BIOS through " Save and exit setup"and, if you did everything right, then wait until this program loads instead of the operating system.
Option 2. If your bios looks like this:

Then you just go to the tab Boot, and then set everything in the same way as in the pictures above (tobish, as the first, choose to boot from disk).
and you did not make a disk, but a flash drive, then in BIOS You will need to select the following option:
Or let's say this:

That is, the name of the flash drive itself and its volume, or something like that, can be indicated. In general, it is not difficult to understand.
Having decided on this, save the changes and exit BIOS starting to download Victoria from the carrier.
Stage II: Downloading the Victoria program and preparing for scanning
When downloading, you will need to select one of the options Victoria. For desktop it would be Victoria for Desktop, for laptop notebook, the remaining items load the shell DOS and file manager Volkov Commander, i.e. in normal cases they are not needed.
Program selection options:

Perhaps, at the first start, you will need to select exactly the hard drive that you want to test (and not the one that is registered in the vcr.ini file - Secondary Master is indicated there in the distribution kit). To do this, press the key P.

A menu with channel names will appear. The selection is made with the cursor keys " up" and " way down". When you move the cursor, an indication (bulbs) is displayed in real time, which allows you to judge the readiness HDD.
A working hard drive will always have 2 lights on: DRSC and DRDY(some may also INX). A red light may be lit in the error registers. AMNF and the rest must be paid off. See the end of the article for more details on the purpose of indicators. After placing the cursor on the desired item, press ENTER.

The last item in this menu is responsible for selecting the hard drive on the external (additional) PCI/ATA/SATA/ controller. After pressing ENTER the search for external controllers and hard drives on them will begin. Only actually present and serviceable hard drives in the position will be determined. MASTER, the rest the system will not notice. When each additional port is found, the following will be displayed in the table:
- Name of the manufacturer of the ATA controller (or its Vendor Code)
- Controller name (or its ID Code)
- Class: EXT / INT / RAID (external, internal, RAID)
- Port address (or a dash if it could not be determined)
- The name of the connected hard drive, if it is available on the channel and is working
All found ports will be numbered. You just have to select the one you need by pressing the appropriate key and confirm Enter"om.
Note:
The program may not find hard drives on some controller models Promise. Next click F2 to "give away" the passport.Passport HDD- this is information hardwired at the factory that characterizes the family of the hard disk and its individual characteristics.
Scanning works closely with the passport, getting all the necessary parameters from it.
Stage III: Scan the disk for errors and problems
Now the most important thing.
To test the surface of the hard drive, press the key F4. Next, a menu will open where you need to set "Linear Reading" and below “Ignore Bad Blocks”(Ignore bad sectors). The selection is made with the key "Space" or arrow keys "Right" and "Left". The scan window looks like this:

Attention!
In the third menu item from the top, such actions as “Record (erase)”, “Record from file” and in the fourth menu item “BB = Erase 256 sect” erase the information on the disk!
Now click again F4 to start scanning. It remains only to wait for its completion.
At the end of the test, if you had no errors, you will see something like this:

What is there to focus on? On the right there is a gradation of sectors from dark gray to red. The more orange and red, the worse it is. If the value of red is especially high, then it is probably time to throw out the disk, especially if the list of defects is full (and not empty as in the screenshot above).
What else is important to understand here:
- If the hard drive freezes due to a malfunction during the scan, the program waits for about 16 seconds, after which it will move to the next block, displaying the icon T(Timeout) in the scan field;
- Continuous delays indicate that the hard drive is not responding to commands. In this case, you can try to send a reset command to its controller by pressing F3(Reset) directly during the scan, sometimes it helps;
- All possible defects and other problems will be described in the block " Defects" or " Messages" on right;
- You can also check the interface. Its check is selected in the third menu item from the top, when you press the key F4"Scan" i.e. where you chose linear reading.
The purpose of the commands is described in sufficient detail in the help system. So press on F1 whenever you are in trouble.
Stage IV: interface verification
The interface check performs a cyclic recording of the data template into the hard drive's buffer memory, then reads from there and compares what was read with what was written. In this case, the reading time from the buffer is measured in the range from 64 before 500 ms.
This test clearly shows what the multitasking of the firmware built into the hard drive is - the reading time of different cycles is different and depends on the model of the hard drive and on its mode of operation. If there is a discrepancy between what was written and what was read, a message is displayed indicating the time by the clock. The presence of such errors indicates a malfunction of the interface or buffer memory of the hard drive, and such a drive is considered potentially dangerous, as it can distort the information stored on it.
To obtain high reliability, you need to run this test for a long time, similar to computer tests. During testing, it is recommended to move IDE cable to diagnose bad contacts, which will be immediately detected by the program.
Note:
Exit the program, button - X.
Coming out of Victoria you find yourself in " Volkov Commander", from which you exit by pressing the key F10 and choosing" YES" respectively. You are then taken to DOS

From where you can exit by pressing Control+Alt+Del. The computer will restart. Don't forget to remove the disk from the drive and return to boot from the HDD.
Useful information on checking and diagnosing a disk through Victoria
Indication of operating modes HDD and error codes for indicator lights.
(Original source - ATA/ATAPI standard)
- BUSY(Busy), - the disk is busy processing the command or "hung". While this light is on, all other indicators are considered invalid and the hard drive can only respond to the "Reset" (F3) command;
- DRDY(Drive Ready), - the drive is ready to receive a command;
- DRSC(Drive Seek Complete), - the drive has successfully completed the installation of the head on the track. Obsolete. On new hard drives, the assignment depends on the previous command;
- INX(Index), - lights up with each revolution of the disc. On some hard drives it is no longer used or may give an incorrect result;
- WRFT(Write Fault), - write error. Obsolete. According to the new standard and, therefore, on new HDDs: "Device Fault" - device failure;
- DRQ(Data Request), - the disk is ready for data exchange via the interface;
- ERR(Error), - an error has occurred (in the error register, you can find the error code).
Error registers:
- AMNF(Address Mark Not Found), - it is impossible to read the sector, usually as a result of a serious hardware problem (for example, on Toshiba and Maxtor HDDs, it indicates a malfunction of the magnetic heads);
- BBK(Bad Block Detected), - found a bad block (bad block);
- UNC(Uncorrectable Data Error), - it was not possible to correct the data with redundant code, the block was recognized as unreadable. It can be either a result of a violation of the data checksum or a result of physical damage to the HDD;
- IDNF(ID Not Found), - sector not identified. Usually talks about the destruction of the microcode or the format of the lower level of the HDD. For serviceable hard drives, such an error occurs when trying to access a non-existent address;
- ABRT(Aborted Command), - the hard drive (disk) rejected the command as a result of a malfunction or the command is not supported by this HDD (password, outdated or too new model, etc.);
- T0NF(Track 0 Not Found), - it is impossible to recalibrate to the starting cylinder of the working area. On modern HDDs, it indicates a malfunction of the microcode or magnetic heads.
This is a necessary minimum that is worth knowing and understanding. For everything else, you need to use the brain, and questions can be asked in the comments or on ours.
Using Victoria 4.46b under Windows. Instructions for checking disks
Now let's talk about using the latest official version of the program under Windows, namely 4.46 .
Having carefully studied SMART and parameters in it, go to the tab Tests. In terms of its functionality, it is generally similar to what we did in the first part of the article:

To run these same tests, you need to click on the button Passp to get information about the drive we're testing (you can select it from the standard if you need another) and then start.

During the check, normal, faulty, problematic and other sectors will be identified, the number of which you can see both in the column on the right and in the log below (in particular, there will be more detailed information about the sectors of the beginning of a particular block, etc.). It remains only to analyze all this and decide what to do with the disk next.
In a nutshell about working with the program from under Windows, perhaps, everything. If something is not clear, then first read the article in its entirety, then look at the comments to it, well, if something is still not clear, then as mentioned above, please contact us, for example, on the forum or in the same comments .
We're moving on to the afterword.
Afterword
This is how pies are made.
Often such diagnostics are needed in the event of the appearance, tapping of the hard drive or any other suspicions that the problem of incorrect operation (in particular, say, partial data loss) lies precisely in the HDD.
Stay tuned and all that. Here you are always happy to help as well;)
PS: For the existence of this article, special thanks to our BSOD-master under the nickname "DJON0316".
Victoria or Victoria is a popular program for analyzing and recovering hard disk sectors. Suitable for testing equipment directly through ports. Unlike other similar software, it is endowed with a convenient visual display of blocks during scanning. Can be used on all versions of the Windows operating system.
The program has wide functionality and thanks to an intuitive interface can be used by professionals and ordinary users. Suitable not only for identifying unstable and broken sectors, but also for their "treatment".
Tip: Initially, Victoria is distributed in English. If you need a Russian version of the program, install the crack.
Stage 1: Getting SMART data
Before you start recovery, you need to analyze the disk. Even if before that you have already checked the HDD through other software and are sure that there is a problem. Procedure:

Data for the hard drive will appear on the same tab almost instantly. Particular attention should be paid to the point Health- he is responsible for the overall "health" of the disk. The next most important parameter is Raw. It is here that the number of “broken” sectors is noted.
Stage 2: Conducting the test
If the SMART analysis revealed a large number of unstable areas or the parameter Health yellow or red, further analysis is required. For this:

Victoria remembers the area where the operation was stopped. Therefore, the next time the test will not start from the first sector, but from the moment at which the test was interrupted.
Stage 3: Disk Recovery
If, after testing, the program managed to identify a large percentage of unstable sectors (the response from which was not received within the specified time), then you can try to cure them. For this:

The duration of the procedure depends on the size of the hard disk and the total number of unstable sectors. As a rule, with the help of Victoria it is possible to replace or restore up to 10% of faulty sections. If the main cause of failures is system errors, then this number may be higher.
Victoria can be used to perform SMART analysis and overwrite unstable HDD areas. If the percentage of bad sectors is too high, the program will allow you to reduce it to normal limits. But only if the cause of the errors is software.