How to protect your wifi from other people's access. How to protect your router or secure wi-fi at home
Today there will be a fairly large post on how to create a secure Wi-Fi network at home, protect home computers connected to this network, smartphones and tablets from hacking, using the RT-N12VP as an example.
So, let’s first understand that the security of your wireless network is determined by its weakest link. Today we'll look at the basic security settings you should have.
Let’s assume that at home you have 2 desktop computers, 2 laptops, 3 tablets and 4 smartphones. I’m not talking about other things, such as TV set-top boxes, wi-fi MFPs and media center servers on Android.
Check that you have antivirus installed on all devices.
This is important. If one of the devices is infected, then the others will be infected in the near future. Thus, Android smartphones can distribute advertising viruses over a local network with great success.
Disable automatic search for networks on mobile devices. The fact is that you may well become a victim of scammers who deliberately create open access points for the purpose of stealing data.
Clear the list of networks remembered by your devices. Leave only familiar secure networks: home, work.
To prevent theft of funds, “diversion” of email accounts, social networks and other sites, use two-factor authentication where possible.
Well, you protected your devices and didn’t fall for the scammers with “free” wi-fi. What's next? Setting up secure wi-fi.
The center of your wi-fi universe in your apartment is your access point (router). In the vast majority of cases, it is protected only by a password and login. Let's try to make your home Wi-Fi network more secure.
Install - Authentication method(security level) — WPA2-Personal
WPA-PSK key(network password) - something like this FD5#2dsa/dSx8z0*65FdqZzb38. Yes, such a password is difficult to remember, but also more difficult to guess. The fact is that there are programs for selecting wi-fi passwords using brute force. Selecting a password in this case is a matter of time. You can even download a similar program to your smartphone, for example, and try how long it will take before you guess the password to your network.

Go to settings Wireless network — Wireless MAC Address Filter
The Wireless MAC Address Filter allows you to control packets from devices with a specific MAC address on a wireless LAN.
Simply put, only those devices whose MAC addresses are allowed to connect will be able to connect to your access point. How can I find out these addresses? You can look in the device settings and enter it into the router settings. You can turn on Wi-Fi on each one one by one, check the data with the data displayed in the router’s network map and enter these addresses into the Wireless MAC Address Filter.
On an Android smartphone, the MAC address is located Settings -> About the phone -> General information ->Wi-Fi MAC address.

If you live alone, or at least there is a period of time when you do not use the wireless network, you can turn it off. These settings are located in the section Wireless network — Professionally

Also in the section Administration —System disable access via Telnet And web access from WAN. This will make it difficult to connect to the router remotely. If there is a firewall in the settings, then enable it.
To be continued.
(3 ratings, average: 4,33 out of 5)
Anton Tretyak Anton Tretyak [email protected] Administrator website - reviews, instructions, life hacks

As practice shows, most users forget or neglect protecting their home network immediately after setting a Wi-Fi password.
Securing your wireless network is not the easiest task, but it is a very important task.
Having gained access to your network, an attacker can post illegal content with impunity or take over your channel and significantly reduce the speed of your connection, for which you, by the way, pay. It can also access not only your computer, but all devices on your network.
Instead of tempting fate, let's go through simple and obvious activities that users often neglect.

Hiding the SSID
The network name or SSID (Service Set Identifier) that we see when scanning the area around us for Wi-Fi. Knowing this network name, you can connect to a particular Wi-Fi network. By default, routers and access points show your network's SSID to everyone. However, it can be disabled in the section of your router or access point. There is an option in this section “enable SSID” or “Disable SSID”. We check or uncheck the box, depending on the name of the option in the corresponding router settings.
Enable encryption
The next point is channel encryption. This option is also located in the section “Wireless Settings” and is called “Encryption settings”. Expand the drop-down list and see about 5 options to choose from ( depending on the router model). How do some types of encryption differ from others?
WEP (WIRED EQUIVALENT PRIVACY).
Came out back in the late 90s and is one of the weakest types of encryption. In many modern routers, this type of encryption is completely excluded from the list of possible encryption options. The main problem with WEP is that it was designed incorrectly. WEP actually transmits several bytes of the encryption key(password) along with each data packet. Thus, regardless of the complexity of the password, you can hack any access point encrypted using WEP by intercepting a sufficient number of packets to crack the password.
WPS/QSS
WPS, also known as QSS, allows you to forget about the password and connect to the network by simply pressing a button on the router. WPS allows a client to connect to an access point using an 8-character code consisting of numbers. But not everything is so rosy. By using only numbers, The cryptographic strength of WPS is much lower than that of WEP and gaining access to your network will not be difficult.
WPA and WPA2 (WI-FI PROTECTED ACCESS)
Some of the most modern types of encryption at the moment and new ones have not yet been invented. WPA/WPA2 support two different initial authentication modes (password verification for client access to the network) - PSK And Enterprise.
WPA PSK or WPA Personal- This is the most common encryption option for home Wi-Fi networks. Connection to the network is carried out using a single password, which is entered on the device when connecting.
WPA Enterprise differs from WPA Personal in that its use requires a separate server - RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service). Essentially, a RADIUS server is a remote user authentication service that verifies user credentials for authentication.
Setting up a MAC address filter
The most radical way to secure your home Wi-Fi network is to set up device filtering by MAC address. A MAC address is a unique identifier for your device on the network. Using it, you can filter devices that are allowed access to your network or vice versa.
We go to the router settings section, which is called “MAC Filtering”. In it we add MAC addresses that can log in to your network. The MAC address of your device can be viewed either in the properties of the wireless connection, in the section "additionally", if it is a computer, or in the settings of a smartphone or tablet, in the section “About the device”. The MAC address consists of 6 blocks of 2 digits in hexadecimal number system, separated by hyphens. For example: A0-23-1D-14-8C-C9.
Enable guest access
By restricting network access by MAC address, you will significantly increase the security level of your network. But what about friends and acquaintances who want to access the Internet through your connection, from their smartphones or tablets? Adding the MAC address of each device is clearly longer than just giving the Wi-Fi password. In this case, most modern routers provide guest access. Guest access means that the router creates a separate network with its own password, which has nothing to do with your home. You can enable guest access (if available) in the section “Home Network Settings” or in “wireless network settings”.
Disabling remote administration
Some wireless routers are equipped with a remote administration function via the Internet. Most users have no need for this feature, and leaving it enabled creates an additional entry point that attackers can use to gain access to your Wi-Fi network. It is also worth disabling the ability to configure the router via Wi-Fi. Changes to the router settings after its initial setup are made very rarely, so you shouldn’t leave another security hole. This function is worth looking in the section security (network security).
The measures described above to improve the security of your Wi-Fi network cannot guarantee absolute protection of your network. Don't neglect prevention and occasionally view the list of connected devices to your network. In the router management interface you can find information about which devices have been or are connected to your network.

We use Wi-Fi not only at home or at work. Do not forget about the dangers of using public Wi-Fi networks in cafes, shopping malls, airports and other public places. We all love free free Wi-Fi, surfing social networks, checking emails over a cup of coffee, or just browsing through our loved ones while waiting to board a flight at the airport. Places with free Wi-Fi attract cyber fraudsters because huge amounts of information flow through them, and anyone can use hacking tools.
The most common attack options and threats in public Wi-Fi networks are:
Sniffing– interception of data in a wi-fi network. By intercepting packets on the way from your device to the router, an attacker can intercept absolutely any information, including logins and passwords for websites.
Sidejacking– wedging into the communication channel between your device and the router. Many sites have secure protocols ( https://) are used only on a page with authorization, after which communication is established through an insecure connection ( http://). After the authorization process, the user's device receives a randomly generated session ID. By intercepting this identifier, the attacker gains full access to the account without the need to intercept the login and password.
Ewil twin– a network created by an attacker who is located near you. Having created such a network, he can only wait for someone to connect to it. Accordingly, all information about all your actions will pass through the attacker’s laptop.
What can we advise if you decide to work from a coffee shop or airport? The recommendations are again generally known, but few people follow them.
- Disable automatic connection of the device to Wi-Fi points. Select a Wi-Fi network manually.
- Look at all available Wi-Fi networks that offer Wi-Fi service to choose one that uses strong security settings.
- We avoid connecting to access points with suspicious names (for example, FreeInternet, FreeWiFi, Dan’s_Point) and disabled encryption.
- Choose access points with WPA/WPA2 encryption enabled (the password can always be obtained from the owner of the public access point).
- Do not carry out financial transactions, purchases in online stores, or check work and personal email while on a public Wi-Fi network. Choose a more secure network for this, and if possible, “share” your Wi-Fi network from your phone.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks to transmit confidential information.
- Be attentive to the people around you. Make sure no one is spying on you when you enter logins, passwords and other confidential information.
- Turn off the Wi-Fi adapter if you do not need to connect to the network (this will save battery power).
Remember! Attackers use the human factor to hack, and only then resort to complex technical manipulations. Be vigilant and do not forget basic measures to protect your devices and data.
Password and MAC address filtering should protect you from hacking. In fact, safety largely depends on your caution. Inappropriate security methods, uncomplicated passwords, and a careless attitude toward strangers on your home network provide attackers with additional attack opportunities. In this article, you will learn how to crack a WEP password, why you should abandon filters, and how to secure your wireless network from all sides.
Protection from uninvited guests
Your network is not secure, therefore, sooner or later, an outsider will connect to your wireless network - perhaps not even on purpose, since smartphones and tablets can automatically connect to unsecured networks. If he just opens several sites, then, most likely, nothing bad will happen except for the consumption of traffic. The situation will become more complicated if a guest starts downloading illegal content through your Internet connection.
If you have not yet taken any security measures, then go to the router interface through a browser and change your network access data. The router address usually looks like: http://192.168.1.1. If this is not the case, then you can find out the IP address of your network device through the command line. In the Windows 7 operating system, click on the “Start” button and enter the “cmd” command in the search bar. Call up the network settings with the “ipconfig” command and find the “Default gateway” line. The specified IP is the address of your router, which must be entered in the address bar of the browser. The location of your router's security settings varies by manufacturer. As a rule, they are located in a section with the name “WLAN | Safety".
If your wireless network uses an unsecured connection, you should be especially careful with content that is located in shared folders, since if it is not protected, it will be available to other users. At the same time, in the Windows XP Home operating system, the situation with shared access is simply catastrophic: by default, passwords cannot be set here at all - this function is present only in the professional version. Instead, all network requests are made through an unsecured guest account. You can secure your network in Windows XP using a small manipulation: launch the command line, enter “net user guest YourNewPassword” and confirm the operation by pressing the “Enter” key. After restarting Windows, you will be able to access network resources only if you have a password; however, finer tuning in this version of the OS, unfortunately, is not possible. Managing sharing settings is much more convenient in Windows 7. Here, to limit the number of users, just go to the “Network and Sharing Center” in the Control Panel and create a password-protected home group.
The lack of proper protection in a wireless network is a source of other dangers, since hackers can use special programs (sniffers) to identify all unprotected connections. This way, it will be easy for hackers to intercept your identification data from various services.
Hackers
As before, the two most popular security methods today are MAC address filtering and hiding the SSID (network name): these security measures will not keep you safe. In order to identify the network name, an attacker only needs a WLAN adapter, which switches to monitoring mode using a modified driver, and a sniffer - for example, Kismet. The attacker monitors the network until a user (client) connects to it. It then manipulates the data packets and thereby kicks the client off the network. When the user reconnects, the attacker sees the network name. It seems complicated, but in fact the whole process only takes a few minutes. Bypassing the MAC filter is also easy: the attacker determines the MAC address and assigns it to his device. Thus, the connection of an outsider remains unnoticed by the network owner.
If your device only supports WEP encryption, take immediate action - such a password can be cracked even by non-professionals in a few minutes.
Particularly popular among cyber fraudsters is the Aircrack-ng software package, which, in addition to the sniffer, includes an application for downloading and modifying WLAN adapter drivers, and also allows you to recover the WEP key. Well-known hacking methods are PTW and FMS/KoreK attacks, in which traffic is intercepted and a WEP key is calculated based on its analysis. In this situation, you have only two options: first, you should look for the latest firmware for your device, which will support the latest encryption methods. If the manufacturer does not provide updates, it is better to refuse to use such a device, because in doing so you are jeopardizing the security of your home network.
The popular advice to reduce Wi-Fi range only gives the appearance of protection. Neighbors will still be able to connect to your network, but attackers often use Wi-Fi adapters with a longer range.
Public hotspots
Places with free Wi-Fi attract cyber fraudsters because huge amounts of information pass through them, and anyone can use hacking tools. Public hotspots can be found in cafes, hotels and other public places. But other users of the same networks can intercept your data and, for example, take control of your accounts on various web services.
Cookie Protection. Some attack methods are truly so simple that anyone can use them. The Firesheep extension for the Firefox browser automatically reads and lists the accounts of other users, including Amazon, Google, Facebook and Twitter. If a hacker clicks on one of the entries in the list, he will immediately have full access to the account and will be able to change the user's data at his discretion. Firesheep does not crack passwords, but only copies active, unencrypted cookies. To protect yourself from such interceptions, you should use the special HTTPS Everywhere add-on for Firefox. This extension forces online services to always use an encrypted connection via HTTPS if supported by the service provider's server.
Android protection. In the recent past, widespread attention has been drawn to a flaw in the Android operating system that could allow scammers to gain access to your accounts in services such as Picasa and Google Calendar, as well as read your contacts. Google fixed this vulnerability in Android 2.3.4, but most devices previously purchased by users have older versions of the system installed. To protect them, you can use the SyncGuard application.
WPA 2
The best protection is provided by WPA2 technology, which has been used by computer equipment manufacturers since 2004. Most devices support this type of encryption. But, like other technologies, WPA2 also has its weak point: using a dictionary attack or the bruteforce method, hackers can crack passwords - however, only if they are unreliable. Dictionaries simply go through the keys stored in their databases - as a rule, all possible combinations of numbers and names. Passwords like “1234” or “Ivanov” are guessed so quickly that the hacker’s computer doesn’t even have time to warm up.
The bruteforce method does not involve using a ready-made database, but, on the contrary, selecting a password by listing all possible combinations of characters. In this way, an attacker can calculate any key - the only question is how long it will take him. NASA, in its security guidelines, recommends a password of at least eight characters, and preferably sixteen. First of all, it is important that it consists of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers and special characters. It would take a hacker decades to crack such a password.
Your network is not yet fully protected, since all users within it have access to your router and can make changes to its settings. Some devices provide additional security features that you should also take advantage of.
First of all, disable the ability to manipulate the router via Wi-Fi. Unfortunately, this feature is only available on certain devices, such as Linksys routers. All modern router models also have the ability to set a password for the management interface, which allows you to restrict access to settings.
Like any program, the router firmware is imperfect - small flaws or critical holes in the security system are not excluded. Usually information about this instantly spreads across the Internet. Check regularly for new firmware for your router (some models even have an automatic update feature). Another advantage of flashing firmware is that it can add new functions to the device.
Periodic analysis of network traffic helps to recognize the presence of uninvited guests. In the router management interface you can find information about which devices connected to your network and when. It is more difficult to find out how much data a particular user has downloaded.
Guest access - a means of protecting your home network
If you protect your router with a strong password using WPA2 encryption, you will no longer be in any danger. But only until you share your password with other users. Friends and acquaintances who, with their smartphones, tablets or laptops, want to access the Internet through your connection are a risk factor. For example, the possibility that their devices are infected with malware cannot be ruled out. However, you won't have to refuse your friends because of this, since top-end router models, such as the Belkin N or Netgear WNDR3700, provide guest access specifically for such cases. The advantage of this mode is that the router creates a separate network with its own password, and the home one is not used.
Security Key Reliability
WEP (WIRED EQUIVALENT PRIVACY). Uses a pseudo-random number generator (RC4 algorithm) to obtain the key, as well as initialization vectors. Since the latter component is not encrypted, it is possible for third parties to intervene and recreate the WEP key.
WPA (WI-FI PROTECTED ACCESS) Based on the WEP mechanism, but offers a dynamic key for enhanced security. Keys generated using the TKIP algorithm can be cracked using the Bek-Tevs or Ohigashi-Moriya attack. To do this, individual packets are decrypted, manipulated, and sent back to the network.
WPA2 (WI-FI PROTECTED ACCESS 2) Uses the reliable AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) algorithm for encryption. Along with TKIP, the CCMP protocol (Counter-Mode/CBC-MAC Protocol) has been added, which is also based on the AES algorithm. Until now, a network protected by this technology could not be hacked. The only option for hackers is a dictionary attack or “brute force method”, where the key is guessed by guessing, but with a complex password it is impossible to guess it.
Hello! I decided to prepare an article in which to collect all the basic and most importantly effective tips and answer your question, how to protect a Wi-Fi network. Who will we protect from? From neighbors, of course, but if you need to protect your Wi-Fi network in the office, then from colleagues from a neighboring company :). But seriously, the issue of protecting wireless networks is very relevant now, I drew conclusions from the article in which I described it. The article quickly became popular and received many comments.
Set a password to access the Wi-Fi router settings
This is the first thing you need to do when setting up security for your wireless Wi-Fi network. In the router settings, look for the “System Tools” tab, then go to the “Password” tab.

Enter the old login and password, then in the form below enter the new access name and the new password twice. Create a good and complex password. Consisting of letters and numbers. And most importantly, remember it yourself :). To save, click “Save”. We continue to configure Wi-Fi network protection.
Set a password for the Wi-Fi network and set the encryption type
It is imperative that you specify the type of encryption you will use for the network and set a strong password. Well, unless you have some kind of cafe and you want to provide open access to Wi-Fi for visitors.
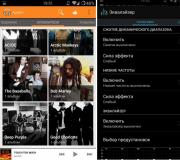
Go to the “Wireless” tab, and “Wireless Security”. Next to the WPA/WPA2 – Personal protocol, put a check mark, set the settings as in the screenshot below and in the line opposite “PSK Password:” we come up with a good password. This password will be used to connect to Wi-Fi. To save, click “Save”.

The router will offer to reboot it, but if you are still making settings, you don’t have to reboot for now. But the new settings will only work after a reboot.
Another great way to protect yourself. We hide the name of the Wi-Fi network, and you can connect to it only if you know what it is called. Your network will not appear in the list of available networks.
We search and go to the “Wireless” tab. And in order to hide the SSID, simply uncheck the “Enable SSID Broadcast” item. That's it, it's simple. Click the “Save” button to save the changes.

Enable device filtering by MAC address
Enabling this function will allow you to connect to the router only those devices whose MAC addresses are specified in the settings and are allowed. This is very effective protection, but if you often connect new devices, it will not be very convenient to go into the router settings and enter the MAC address of the device every time.
First you need to find out the MAC addresses of the devices that you want to allow to connect to the Wi-Fi network. They can be viewed in the settings, read more. If this is a phone or tablet, then you can see the address in the settings, in the “About phone” section. And if the device is already connected to the router, then all the necessary information can be found on the “DHCP” - “DHCP Clients List” tab.
So, go to the “Wireless” tab, and go to “Wireless MAC Filtering”. First, enable this service by clicking on the “Enable” button. Then check the box next to the item “Allow the stations specified by any enabled entries in the list to access.”. This means that only devices that are on the list will be able to connect to Wi-Fi.

And click the “Add New...” button in order to add the MAC addresses of devices that need to be allowed access. Enter the MAC address, description (optional), leave the status Enable (allow) and click the “Save” button.

In this way we add all the devices that you want to allow to connect to your router.
Disable QSS (WPS) service
I wrote in detail about this service and how to use it in the article. But if you do not connect new devices very often and it is not difficult for you to enter the password for the Wi-Fi network, then it is better to disable this service.
To disable, go to the “QSS” tab; for you it may also be called “WPS”, or something like that. And click the “Disabled QSS” button.

This was the last point that I advise you to do to completely protect the Wi-Fi network on your router. All that remains is to reboot the router by clicking on the “click here” link, or do it with a button on the router itself.
That's all friends, that's all I wanted to advise you to protect your wireless network. I hope that the information I have prepared for you will be useful to you. Good luck!
Also on the site:
How to protect a Wi-Fi network? Basic and effective tips
updated: February 7, 2018 by: adminNowadays, most apartments and houses have more than one device that is connected to the Internet. This has led to the popularity of routers and wireless access points, which have almost completely replaced connecting an Internet provider cable directly to a single computer. Now the Internet service provider wire is included in a special device that allows you to use the same connection for several computers at once, as well as connect mobile devices, laptops and regular computers via Wi-Fi, combining them into a local network.
We have routers at home, in a warm and cozy place, and this gives rise to a false feeling that the routers are safe. This is not at all true, each router stands on the seven winds - in a very aggressive environment: anyone (literally ANYONE) within reach of the wireless signal can interact with your router, record transmitted traffic; You also need to remember that routers have access to the Internet, where numerous automated scanners can scan ports, running services, try passwords, and perform exploits against your router dozens of times a day.
Your router needs protection - without your help it could become a victim of hackers, this article will tell you how how to protect and configure a Wi-Fi router so that it cannot be hacked.
What can hackers get by hacking a Wi-Fi router?
Many users take router security lightly because they do not understand the dangers that can result from hacking a router. It is curious that most users understand the danger of having their computer hacked, since an attacker can gain access to their personal data, photos, and passwords. It is very important to understand that hacking a router is a prior step to hacking a computer. Having penetrated the router, a hacker can:
- perform a man-in-the-middle attack, which is aimed at intercepting passwords and other data that you transmit over the network;
- carry out a man-in-the-middle attack aimed at infecting a user's computer with a backdoor or Trojan;
- carry out phishing attacks aimed at obtaining logins and passwords from websites, extorting money, infecting a computer with a backdoor or Trojan;
- monitor users' network activity;
- block the Internet connection completely or to individual sites;
- use the Internet connection for criminal activities (law enforcement agencies will see your IP as the address of a cybercriminal);
- access webcams and other peripheral equipment connected to your router
- make changes to the router firmware.
Hacking a router is a serious threat that can lead to serious consequences for the user.
How to get into the router settings
In the vast majority of cases, a web interface is used to manage routers, i.e. You can make all settings directly from the browser. Your computer and your router are on the same local network (it doesn't matter whether you use Wi-Fi or a wire). To get “inside” your router, type in your browser
If this address does not work, then sometimes it can be
You will be greeted with a form to enter your username and password. They can be viewed in the device passport, on the box, on the case. Or just look for the default (factory) credentials for your router on the Internet.
Each model has its own interface design and grouping of settings, but usually the “Wireless network”, “Local network” and “Internet” items are always present. Menu items and settings may be named a little differently, but once you understand the meaning of the setting, you can easily find it in your home.
Recommendations for protecting your router and Wi-Fi access point from hacking

Use a password to access your network
Do not leave your wireless network “Open”, select the encryption (authentication method) WPA or WPA2.
Stop using the WEP algorithm
WEP is an outdated, largely unused Wi-Fi security algorithm. It can be hacked in minutes. However, there are still access points that use WEP, so check yours and if it uses WEP for encryption, switch to WPA or WPA2.
Disable WPS
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) provides an easy, but not secure, way to create a wireless network. Depending on the degree of vulnerability, the WPS, and then the Wi-Fi password, can be hacked in a day or even in a matter of minutes.
Set a strong password
Since by its very nature a Wi-Fi network is accessible to anyone within its range, anyone can try to connect to it by trying different passwords (called online brute force). Another technique is also popular, which is based not on connection attempts, but on capturing certain data that the legitimate user and the access point exchange at the time of connection and their subsequent hacking (offline brute force). The use of the latter allows you to brute force passwords at a speed of tens and hundreds of thousands per second. You can only protect yourself from such an attack by setting a long and complex password.
The following rules will allow you to be almost guaranteed to protect yourself from any brute force hacking:
- use a long password. The Wi-Fi password cannot be less than eight characters. If possible, try to use passwords of 10 or more characters;
- the password should not be a meaningful phrase or consist of several combined meaningful words, since such a password option can be hacked using a dictionary;
- use four classes of characters in your password: numbers, capital and small letters, punctuation marks;
- From time to time, for example, once every few months, change your password to a new one.
The screenshot above shows that routers often use generated passwords consisting of eight characters and including three classes of characters (capital and small letters, numbers): L95atyz7, 6rQTeRBb, YssvPT4m, WJ5btEX3, dn8MVX7T. To crack such passwords on a typical home computer, it will take 1-3 years of continuous brute force. BUT by assembling a computer on several top-end video cards (by making something like a “farm” for mining), a complete search of such a password can be reduced to one or several months. In my opinion, such passwords cannot be considered reliable. As already mentioned, add a fourth character class (syntax marks) and increase the number of characters - this will guarantee that your Wi-Fi network will not be hacked even with the use of very powerful equipment.
Check your 5 GHz network settings
Many users do not know that their router operates in two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. If you secure one range but forget about another, the attacker can take advantage of this. Set a strong password for the 5 GHz network, disable WPS for it. If you do not use the 5 GHz band, you can simply turn it off.
Set a strong password to log into the router admin area
As already mentioned, your router is connected to local and global networks, where anyone can try to connect to it. To prevent an attacker from guessing your password, set a long password using different character classes.
Change the admin name
Change the username from Admin/admin to another, less predictable one - this will further complicate the task of guessing the password.
Disable access to the router control panel from the Internet
In the vast majority of cases, you only need access to the router’s administration panel from the local network. If you do not need access to the router settings from an external network (from the Internet), then disable it; this will prevent an attacker from trying to guess the login password. This setting may be called "Enable Web Access from WAN".
Update your router's firmware
Even with a strong password, an attacker can gain access to the router or obtain the password in clear text if the router contains a vulnerability. New firmware from manufacturers should eliminate vulnerabilities and other errors, improve stability and functionality, so regularly (every few months) check for new firmware and update it on your router.
Search for vulnerabilities in the router
Unfortunately, sometimes vulnerabilities are found after the manufacturer has stopped supporting the router. This can lead to a situation where hackers are aware of a vulnerability in your router, but there are no firmware updates.
You can check your router for vulnerabilities using Router Scan by Stas’M. It is a fairly easy to use GUI program.
If you are familiar with Linux, you can use a similar program called RouterSploit, which may have exploits that Router Scan does not. Instructions for use:
If your router turns out to be vulnerable without the ability to update the firmware, it is recommended that you stop using it and replace it with a new one.
Disable unused network services
The more complex the device, the more potential points for a hacker to apply his efforts. Many of the online services and advanced features are not used by most users, and some of them also contain known vulnerabilities. Therefore, disable SSH, FTP, Telnet, Internet file sharing (for example, AiDisk), file/media server (for example, UPnP), SMB (Samba), TFTP, IPv6 and others that you do not need.
Enable HTTPS for administrative connections
On most routers it is disabled by default. This setting will allow you to prevent the interception of your router admin password if you connect to it from the Internet, or during man-in-the-middle attacks if the attacker has already penetrated your local network.
Log out (log out) when you are done using the router
Simply closing the page can leave the login session open on the router.
Enable logging
It's a good habit to check your logs for suspicious activity from time to time. Set the clock and time zone correctly to make logs more accurate.
Check logs, control connected devices
This already applies to identifying a hacked router - this issue will be discussed in more detail below.
Set up a "Guest" network
Many modern routers can create separate guest networks.
Make sure that it only has access to the Internet and not to the local network. Naturally, use WPA2 and, of course, the password should be different, not the same as for your main Wi-Fi.
Additional steps to protect your router
If the previous one is not enough for you, then here are some more tips for you.
Change the default range of IP addresses for your local network
All user routers I've seen have the same local address range. This is 192.168.1.x or 192.168.0.x. This facilitates automated script attacks.
Available ranges:
- Any 10.x.x.x
- Any 192.168.x.x
- 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x
Change the router's default local address
If someone breaks into your network, they know for sure that your router address is x.x.x.1 or x.x.x.254, making it difficult for them.
Limit administrative access over the wireless network
It's not for everyone. For example, it may be that absolutely all computers are connected only via a wireless network. But if this can be done, it will greatly complicate the attacker's task.
Using a MAC filter
This is not an effective method of defense, since an attacker can easily find out the MAC addresses being skipped and spoof them. There is no need to rely on this protection.
Hiding the network
Ineffective from a safety point of view. Does not worsen security, but does not increase it either, since an attacker can easily find out the name of the network.
Signs of a Wi-Fi router being hacked
Changing router settings without your knowledge
If illegitimate users have changed any settings, especially the password for entering the administration panel, DNS, VPN settings, then this is a sign that a hacker has gained access to your router.
Control devices connected to your local network
For this, programs such as NetworkConnectLog and Wireless Network Watcher () can be used.
An unauthorized connection means your network is compromised.
View the router log
If your router supports logging that records device administrator logins, review it regularly to identify suspicious activity.
Detecting man-in-the-middle attacks and strange network disruptions
Advanced users, in addition to detecting new devices on the network, can also take actions to identify attacks that have begun against them ")".
Strange disturbances in network operation may also indicate changes in the settings of network equipment and interception/modification of traffic by the attacker.