Download the program for low formatting. Quick or Full Format? The best programs for low-level formatting
Have a nice time!
It’s not uncommon for all sorts of troubles to happen with SD cards and USB flash drives: sometimes they can’t be read, sometimes copying takes too long, sometimes various kinds of errors appear (what, what formatting is required, etc.). Moreover, this sometimes happens out of the blue...
In this article, I want to recommend a dozen utilities that have helped me out more than once or twice. With their help, you can work with flash drives and drives from different manufacturers (Silicon Power, Kingston, Transcend, etc.), i.e. This is a universal software. I think the material will be very helpful to everyone who periodically faces similar problems.
For testing and diagnostics
CrystalDiskMark

A very useful little utility. Allows you to quickly obtain read/write speed data. Supports not only USB flash drives, but also classic HDDs, SSDs, external hard drives and other drives (which Windows sees).
Note: in most cases, they are guided by the first line “Sec” (sequential read record speed). Read - reading, Write - writing.
USB Flash Benchmark

Another utility for testing the speed of flash drives. Allows you to get not only some numbers, but also compare them with other drives (i.e. evaluate your flash drive with other device models). This can be done due to the fact that the test results are saved on the website of the same name (along with flash drive models).
By the way! If you are thinking of buying a fast flash drive, just go to the website http://usbflashspeed.com/ and look at the top 10. This way you can acquire what other people have already experienced in practice!
H2testw
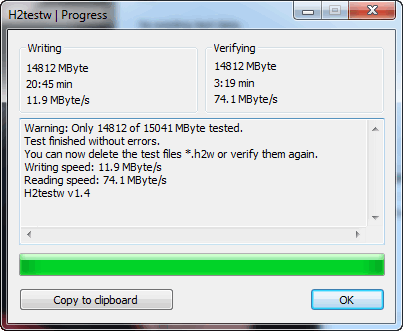
A small utility from German programmers. Designed to scan USB drives for their actual capacity (approx. : some flash drives, for example, from Chinese manufacturers, come with a “fake” inflated volume) . In these cases, it is enough to run the flash drive using H2testw, and then format it correctly.
How to find out the real capacity of a flash drive and restore its functionality (using H2testw) -
Flash Memory Toolkit

Flash Memory Toolkit is a good package for servicing USB devices. Allows you to perform a whole range of the most necessary actions:
- testing drives for errors when reading and writing;
- data recovery from flash drives;
- viewing properties and characteristics;
- the ability to create a backup flash drive;
- low-level drive speed test.
Flashnul
Developer's website: http://shounen.ru/

This program can diagnose and correct many software errors (especially when it is unclear what is happening with the flash drive: that is, no errors are displayed). In addition, it supports almost all flash memory media: USB flash drives, CompactFlash, SD, MMC, MS, XD, etc.
Possibilities:
- reading and writing testing: the availability of each sector of the media will be checked;
- checking the integrity of files located on a USB drive;
- the ability to make an image of the contents on a flash drive (may be useful for data recovery);
- possibility of sector-by-sector recording of an image to a USB device;
- Some operations can be performed for other types of media: HDD, CD, Floppy disk, etc.
ChipEasy

A free and very simple utility for obtaining complete information about a flash drive. It is very useful in cases where the markings on the flash drive itself have been erased (or there were none at all).
What data does ChipEasy provide:
- VID
- manufacturer;
- controller model;
- serial number;
- firmware information;
- memory model;
- Max. current consumption, etc.
Flash Drive Information

The utility is similar to the previous one. Allows you to find out all the information about the drive (flash drive, memory card) in 2 clicks: model, controller, memory, etc.
For formatting and repair
HDD Low Level Format Tool

A program for low-level* formatting of hard drives, SD cards, flash drives and other drives. I would note its “unpretentiousness”: even if other utilities freeze when trying to access a flash drive (or don’t see it), the HDD Low Level Format Tool can help in most cases...
Peculiarities:
- Most manufacturers (Hitachi, Seagate, Samsung, Toshiba, etc.) and interfaces (SATA, IDE, USB, SCSI, Firewire) are supported;
- formatting clears absolutely all information from the disk (partition table, MBR);
- Recovering information from a disk after formatting using HDD Low Level Format Tool is almost impossible!
MyDiskFix

A free small utility designed for low-level formatting of failed flash drives. It is useful in cases where your flash drive cannot be formatted using standard Windows tools, when the flash drive shows the wrong volume, or a recording error occurs.
Note: before formatting in MyDiskFix, you need to find out how many actual working sectors are on your flash drive. This can be done, for example, using the H2Test utility (which I cited above).
USB Disk Storage Format Tool

A small utility for formatting HDD/USB Flash drive (file systems supported: NTFS, FAT, FAT32). By the way, the USB Disk Storage Format Tool does not require installation, and does not freeze if it works with faulty flash drives, from which you need to wait minutes for a response (like, for example, the standard formatting utility in Windows).
Peculiarities:
- fast and safe formatting of the drive;
- when fully formatted through the utility, all data from the flash drive is deleted (later, not a single file from it will be recoverable);
- scanning the drive for errors;
- creating partitions with the FAT 32 file system larger than 32 GB;
- tested with 1000 different flash drives (Compact Flash, CF Card II, Memory Stick Duo Pro, SDHC, SDXC, Thumb Drive, etc.), and various manufacturers (HP, Sony, Lexar, Imation, Toshiba, PNY, ADATA, etc. ).
Format USB Or Flash Drive Software

A specialized utility for working with failed USB drives. Allows you to format and restore the flash drive. I would also note its very simple interface (see screenshot above), and the ability to work without installation.
Peculiarities:
- file system support: FAT, FAT32, eXFAT, NTFS;
- simple and convenient interface;
- possibility of full and quick formatting;
- the ability to “see” drives that the explorer refuses to “show”;
- possibility of integration into the Windows menu;
- Compatible with Windows 7, 8, 10.
Transcend RecoveRx

Multifunctional program: allows you to recover files from flash drives, format them, and protect them with a password. In general, this program is intended for flash drives from the manufacturer Transcend, but I can’t help but note that the formatting option also works for flash drives from other manufacturers.
RecoveRx is a fairly “omnivorous” program: it supports USB flash drives, memory cards, MP3 players, external hard drives (HDD) and solid-state drives (SSD).
JetFlash Recovery Tool

This utility will help in cases where standard Windows tools simply do not see the flash drive. Officially supported USB flash drives are only from Transcend, JetFlash and A-DATA (unofficially - much more).
Important! Keep in mind that during the process of repairing (restoring) a flash drive, the program completely deletes all data from it! If you have the opportunity to save something from a faulty flash drive, do so.
Peculiarities:
- simple and free utility (only 2 buttons!);
- compatible with Windows 7, 8, 10 (also works with older OS Windows XP, 2000 (other OS - operation is not guaranteed));
- Only 3 manufacturers are officially supported: Transcend, A-DATA and JetFlash;
- automatic recovery of the drive (the user only needs to press 1 button);
- low system requirements;
- no utility installation required.
SD Formatter

Formatting a Canon SD card in SD Formatter
This utility is designed to repair and restore memory cards: SD, SDHC, SDXC, microSD. The developers specifically targeted their product to the needs of photographers, videographers, and service specialists for such equipment.
The drive is restored in auto mode. Suitable for a variety of cases: software errors, virus infections, failures, due to improper use, etc.
Note: while working with a flash drive, SD Formatter will delete all data from it!
D-Soft Flash Doctor

A small portable program for diagnosing and repairing broken flash drives (low-level formatting, soft reset). In addition, it can create images from flash drives/memory cards and write them to other storage media.
The program supports the Russian language (since the developer is from Kazakhstan), and is compatible with all modern Windows 7, 8, 10 operating systems.
To recover files from a flash drive
R.Saver

An easy-to-use program for recovering deleted files from various types of media: hard drives, memory cards, flash drives, etc. Can be used for various errors, file system failures, after formatting, virus infection, etc.
Supports NTFS, FAT and ExFAT file systems. For residents of Russia (when used for non-commercial purposes) the program is free.
Important!
You can learn more about working with R.Saver in the article on how to recover photos from a MicroSD memory card or USB flash drive -
Recuva

A file recovery program from the developers of CCleaner (the famous utility for cleaning Windows from junk files).
Recuva allows you to work not only with HDDs, but also with USB flash drives, external drives, SSDs, and memory cards. The program is aimed at the novice user, so its use is very simple.
Peculiarities:
- all actions in the program are performed step by step;
- 2 modes for scanning drives;
- sorting files by their name, size, status, etc.;
- The utility is free;
- Russian is supported;
- Compatible with Windows XP, 7, 8, 10 (32/64 bits).
MiniTool Power Data Recovery

A very powerful program (with unique scanning algorithms) that will allow you to recover data from damaged flash drives, memory cards, external drives, CDs and other drives. Popular file systems are supported: FAT 12/16/32, NTFS.
I would like to note on my own that, in my humble opinion, the program’s algorithms are actually different from other programs of a similar kind, because several times with its help it was possible to recover information when other software simply did not find anything...
Note: in the free version of MiniTool Power Data Recovery, you can only recover 1 GB of information.
Addition!
In general, there are quite a lot of similar programs ( approx. : which can scan the drive and recover some of the deleted files). In one of my previous articles, I already cited a dozen of the most successful free products (most of them work not only with classic HDDs, but also with flash drives). I am posting a link to the article below.
10 free programs for recovering deleted data: files, documents, photos -
That's all for now. Additions to useful and interesting utilities are always welcome.
Formatting is the process by which a data storage area is marked up. This area is called file system, and is a table.
Each square of such a table is called a cluster. And when a file is copied to a flash drive, the clusters are filled with data one by one until the file is completely moved.
If information is frequently rewritten to the device, the clusters begin to fill unevenly, since some of them contain remnants of previous files. And new recorded files can occupy clusters at different ends of the “table”, which slows down the operation of the flash drive.
Formatting resets all parameters and re-marks. This has a positive effect on the speed of the device, because the file system is reset. That is, the “table” is cleared.
Why do you need to format
- To quickly destroy all recorded information
- To “kill” all viruses and traces of their activity
- To resolve errors that occur when opening and writing files
- To speed up the device
- When creating a bootable USB flash drive
Formatting erases all data that was written to the flash drive! Therefore, before running it, be sure to transfer all important files to another location (for example, to your hard drive).
How to quickly format a flash drive
This can be done using standard system tools. They are available in any version of Windows (XP, 7, 8, 10).
1. Insert the flash drive into your computer.
Most likely, an autorun window will open in a second or two. Let's close it.

2. Open Start - Computer.

3. Right-click on the flash drive icon and select “Format...”.

4. Select parameters or leave everything as is.

File system. You are asked to choose one of three. The default is usually Fat32. It is good if small files will be written to the device, as it interacts with them faster. But if you need to write a file larger than 4 GB, then problems arise - Fat32 does not support working with such large files.
NTFS is another matter. This system is capable of working with very large files, even more than 1TB. But with small ones it works a little slower than Fat32.
There is also exFAT. This is an upgraded Fat 32 that can handle files larger than 4GB. However, it is currently only supported on Windows 7 and above, and other devices (such as TVs) and computers running older versions of Windows cannot work with it.
There are more advanced file systems, for example, ext4, but Windows does not yet support anything better than NTFS and exFAT.
So, if you plan to write small files to a flash drive, then you can leave the default file system (Fat32), and if you need to copy individual files larger than 4 GB (for example, a movie) to it, then choose NTFS.
Cluster size. Minimum data size. It is better not to change anything in this field.
Volume label. The name of the device that will be shown during boot. For example, I want the flash drive to appear as "Neumeka". This means that I erase from this field what is suggested and print the name I need. As a result, it will appear like this:

Formatting Methods. Initially, this item is checked for “Quick (cleaning table of contents)”. This method will overwrite the file system, which is usually quite enough.
If you uncheck the box, a full format will be done, which means that the computer will first check the physical surface of the flash drive and if it finds damage, it will fix it. In fact, they will simply disguise themselves and then it will be impossible to write information there. And only after all this will the file system be written.
5. Click “Start”.

The system will warn us that it will destroy all information from the device. We agree and wait for the process to end.

When it finishes, we will see the following window. Click “OK” and close the formatting window.

All! The device is ready for use.
If it didn't work out
Despite the fact that a flash drive is more reliable than a CD and DVD, it still suffers from problems. For example, it may simply not be displayed in “Computer”.
This happens for several reasons:
- File system is damaged
- The device was not formatted by the manufacturer
- The letter of the flash drive matches the letter of the drive already in use by Windows
To eliminate these reasons, go to Start - Control Panel.

Go to “System and Security” and/or “Administration”.


Open "Computer Management".

Click on “Disk Management” on the left side.

The window takes on the following appearance.

Right-click on the flash drive and select “Format...”.

Formatting using the command line
Another formatting method. But in order to use it, you need to know exactly the letter of the flash drive. Otherwise, you may accidentally delete data from another, desired drive.
1. Press the keyboard shortcut Win + R.

2. In the Run window, enter cmd and click OK.

3. In the window that appears, enter format G: /FS:NTFS /Q /V:flashka

- format is a command to start formatting
- G is the drive letter under which your computer recognizes the flash drive (do not confuse it!)
- /FS:NTFS - file system in which you want to format the device. If you want fat32, then enter FS:FAT32
- /Q - quick formatting. If you need the complete one, just don't use this command
- /V:flashka - volume label (this name will be displayed when loading in “Computer”).

When everything is ready, a similar inscription will appear.

Low-level formatting or “flash drive treatment”
This method should only be used if all of the above did not help.
Download and install the HDD LLF Low Level Format Tool program from the official website. During the installation process, select “Continue for free”.

Open the program, select your flash drive and click Continue.

A window with information about the device will appear. Go to the LOW-LEVEL FORMAT tab.

Click on the FORMAT THIS DEVICE button.

A warning appears that all data written to the media will be erased. Click “Yes”.

And we wait for the end of the process: when the window becomes something like this and 100% complete is written.

We close it and do the usual formatting, otherwise the flash drive will not open. To do this, follow the first instructions from this article (Start - Computer - right-click on the flash drive icon - Format...).
FAT32 (File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in August 1996 and was developed to improve the previous version of FAT 16.
Conceptual improvements include increasing the volume size to 8 TB versus 2 GB in FAT 16 and increasing the maximum file size that the file system supports from 2 GB to 4 GB.
What should users do who need to transfer files larger than 4 GB to a flash drive?
Formatting a flash drive:


Low-level formatting of a flash drive
Low-level formatting is used to erase information without the possibility of its recovery .
This approach is important if there was and is confidential data on the flash drive and you need to prevent third parties from accessing it.
Attention! It is important to remember that this procedure should not be abused unless absolutely necessary.
You won't be able to perform low-level formatting using standard Windows tools, so let's download and install the shareware HDD Low Level Format utility.
To perform low-level formatting you must:


How to recover an SD card or USB flash drive if the computer does not see it, does not read or write data? Problems with flash drives are rarely caused by natural wear and tear. More often, problems with them are caused by users ignoring the rules for safely removing the device, experiments with various software in which these flash drives are involved, as well as their initially lousy quality. Below we will consider a list of possible actions carried out in the Windows environment that can solve the problem, unless, of course, the cause lies in a mechanical failure. And we, friends, will go from simple to complex.
- Note: below we will only talk about restoring the functionality of flash drives, but not about saving the data stored on them. This is a separate topic, and there is information about this on the website. Most of the methods proposed below for recovering SD cards and flash drives will lead to the loss of their data.
1. Hardware lock
SD cards, MicroSD adapters and flash drives can be hardware protected from writing data or completely blocked even for reading. On such devices there is a lock switch, which must, accordingly, be set to the “Unlocked” position.

2. Problems not related to the drives themselves
The cause of problems with SD cards and flash drives may be Windows security policy. You need to find out whether access to removable drives is blocked (in whole or in part of writing data to them) by the computer administrator. You also need to check the card reader or USB ports of your computer. If everything is fine with the latter - the card reader reads other SD cards, but problems still arise with the flash drive, no matter how you connect it to other USB ports, move on.
3. Windows Explorer
Standard formatting using Windows Explorer can help in simple cases such as unsuccessful writing of data to a flash drive. Or when for some reason a smartphone, tablet, camera or other device cannot cope with this operation regarding SD cards. In any current version of Windows, in the Explorer window on the drive, call up the context menu and click “Format”.

We leave the original file system and first try a quick format.

If it fails, we repeat the operation, but with full formatting (uncheck the fast box).

4. Windows Disk Management
You can try to perform the formatting procedure in disk management. To launch this tool, enter in the system search field:
diskmgmt.msc
In the disk management window, focusing on the size of the drive, we look for it among the disks connected to the computer. And in the context menu called on it, we launch formatting.

You can immediately select full formatting.

If the flash drive has a partition structure like a hard drive, you must delete each of those partitions. This is done using the “Delete Volume” option in the context menu.

And then, in place of the resulting unallocated space, you need to create a single partition. To do this, in the context menu on this very unallocated space, launch the “Create a new volume” operation and follow the instructions of the step-by-step wizard.

5. Programs for low-level formatting
Standard formatting tools may not help in complex cases, for example, when flash drives are displayed (in the same Explorer or Disk Management) as unrecognized devices with the RAW file system. The latter means that either the Windows environment does not understand the file system of the drive, or there is no file system as such in principle. Actually, this is what causes problems with a flash drive or SD card when it works on other devices, with other operating systems. In such cases, third-party Windows programs designed for so-called low-level formatting will help restore the flash drive.
In fact, low-level formatting is a procedure that is carried out either in the production conditions of flash device manufacturers, or in serious specialized services. Various types of Windows software that claim to perform this kind of operation actually perform a regular full format, but using mechanisms that differ from those used by the operating system. Such programs cope well with flash drive problems if these problems arise at the file system level. Let's look at two of these programs.
HDD Low Level Format Tool
http://hddguru.com/software/HDD-LLF-Low-Level-Format-Tool/
The shareware portable program HDD Low Level Format Tool can format various types of storage media, in particular SD cards and USB flash drives. After unpacking the archive with the program, run it and agree to the license terms.

We choose free use.

Directly in the program window we indicate the problematic drive and click “Continue”.


We confirm the decision.

We wait for the operation to complete and check the operation of the media.

SDFormatter
http://flashboot.ru/files/file/355
A completely free small program called SDFormatter is another tool for so-called low-level formatting. Works with both SD cards and USB flash drives. Install SDFormatter into the system, launch it, and indicate the problematic flash drive in the “Drive” column. Click “Format”.

The program wants to make sure that our intentions are serious, click “Ok.

He asks not to touch the drive while the operation is being performed.

Upon completion, test the flash drive or SD card. If this does not help, repeat the operation with the settings for complete overwriting of sectors (nothing more than full formatting). Press “Option”, select “Full (OverWrite)”. And also click “Format” at the bottom.

If using the above methods it was not possible to revive the flash drive, and it is still under warranty, you need to stop at this stage. And do not take any further action except contact the seller with a request to replace the device. All the actions described below should be resorted to only when, in fact, there is nothing to lose. The instructions below apply to USB flash drives, SD and MicroSD cards. However, in the case of the latter, the likelihood of recovery is extremely low.
6. D-Soft Flash Doctor
D-Soft Flash Doctor performs so-called low-level formatting, and at the same time also detects damaged sectors (cells). Well, and, accordingly, knows how to block them and replace them with backup ones. The program can help when flash drives or SD cards have difficulty reading individual files located on damaged sectors. The program is free and portable. I did not find the official website, but it can be freely downloaded on the Internet.
In the D-Soft Flash Doctor window, the first thing you need to do is run a scan to detect errors.

In my case, there were no damaged (broken) sectors.

But if in your case, friends, the scan results are different and bad sectors are detected, we start the recovery process.

The window for performing this operation promises that the process will not last longer than 10 minutes, but in fact, reassigning bad sectors on a drive with a capacity larger than 4 GB can take quite a long time. So it is better to run the recovery operation at night.

7. Flashing the memory controller
Programs for so-called low-level formatting or their analogues, which in any other form claim to be able to resuscitate all types of SD cards and/or USB flash drives, turn out to be powerless in the event of a software failure of the controller, when it requires flashing. This problem can have different symptoms, but more often it is either the computer does not see the drive completely, or it sees it and can even read the data, but cannot format it by any means. In particular, due to write protection even though the drive is not locked by hardware.
Often, when it is necessary to format a flash drive, users use a standard Windows application. But it has some disadvantages and does not allow you to make fine adjustments to the formatting process. If you need to fix damaged areas of memory or erase information without the possibility of restoring it in the future, it is better to download and install a special utility.
I already wrote about . I also discussed the issue of fast using programs and the command line. Today we will look at low-level formatting.
The concept of low-level formatting
This formatting method is usually chosen when it is necessary to protect information from leakage. Perhaps the user of the flash drive stored some personal data and then gave it to another person for use. To prevent anyone from using data recovery programs, it is necessary to completely erase the information stored in binary form with zeros.
*Low-level formatting* layouts the storage device into sectors and tracks, writes data about the type of file system. As a result of this process, all user information stored on the flash drive disappears without a trace. There is no way to restore it.
Why do low level formatting?
Most often, the reasons for choosing low-level formatting are the following:
— it is necessary to remove applications that have been infected with viruses, and they cannot be removed in any other way;
— if the flash drive is planned to be sold or given to another person for use;
- if the flash drive previously served as a disk on which there was a distribution kit with Linux or this operating system in its installed form;
— if you can’t access the flash drive, it’s not visible in Windows Explorer, and you can’t write any information to it;
— it is necessary to restore damaged memory areas or use backup ones instead.
Low-level formatting program USB Disk Storage Format Tool
This low-level formatting program allows you to perform this process with various settings. If there are broken clusters on a flash drive, it can be used to restore them. Download and run the program. A small window will appear in front of you in which you need to select the device to format and the type of file system.
Also, the application’s capabilities made it possible to name the device after formatting it in a special field called “Volume Label”. There are two ways to format a flash drive here: Quick Format (quick format) and Verbose (deep).
You can also check the disk, which comes with 3 options: error correction, scanning and checking for contamination.
The formatting process of this program is recorded in a log, which is displayed directly in the program window. More experienced users can view the log and determine the cause of the errors.
The disadvantages of the application include the English language and the inability to create a boot disk.
Download a program for low-level formatting of a flash drive— http://www.ixbt.com/news/soft/index.shtml?17/13/73
Low-level formatting in full can only be carried out at the storage device manufacturing plant. But there are special applications. Which are able to almost completely imitate this type of formatting. One of the simplest and at the same time multifunctional programs is the USB Disk Storage Format Tool.



