Find out which RAM is suitable. How to find out what RAM is on your computer
RAM is one of the most important components of any computer and certainly a guarantee of operating speed. In the modern world, even the frequency of the processor does not affect the overall perception of speed as much as RAM. But in order to replace or add this component, you need to thoroughly know all its characteristics - and RAM has a lot of them. So, how do you find out what RAM is in your computer? In this article.
How to find out what RAM is on your computer
RAM has several division branches:
- the first is volume, a fairly obvious characteristic. The more the better, but look at the processor and motherboard - they support the increase up to a certain ceiling;
- the second characteristic is type. An ancient SIMM, a slightly less ancient SDRAM... Well, this is unlikely, of course, although it is not excluded. And modern DDR standards - from first to fourth;
- and finally the memory frequency. Here, as in the case of processor frequency, the higher the better. However, again make sure that your processor runs at this frequency. If it doesn't start, it will be quite a shame.
So, let's start studying these signs.

Simple inspection
The most obvious way to find out your computer's RAM type is without even turning it on. In many cases, it allows you to determine the required characteristics with absolute accuracy, but it also has a number of significant disadvantages. You will have to open the computer - for some this is a significant stopping factor. The sticker on the memory stick may not correspond to reality, be insufficiently informative, as with many not very well-known manufacturers, or be completely absent. However, this method can be used quite well.

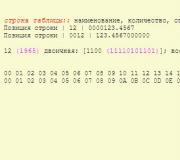
Note. There is another labeling standard. Pay attention to the picture above. In brackets on the sticker you can see the inscription PC3 10600. These are nothing more than encoded characteristics, excluding volume. PC3 - DDR3, 10600 - frequency. To get the usual value in megahertz, you need to divide this number by 8. You get the familiar 1333.
You can also add that the type of memory can be determined by the location of the contacts and cutouts on the bottom edge, but this is a rather complicated and unnecessary method, so we will bypass it.
Diagnostics in BIOS
This is also quite a convenient method. There is no need to open the computer, but at the same time there is no need to clutter the system with all kinds of diagnostic programs. Simple and tasteful. On the downside, not all BIOSes can display complete information about memory, but this is a rare case these days.


How to decipher such an inscription - see the note to the first method.
Operating system tools
The simplest of all methods. However, it is also the most limited. If it is enough for you to know only how much RAM you have, this is for you, because on its own the system cannot determine either the frequency, much less the type of RAM. But this is only about Windows - macOS can do more.
In the case of macOS:

If you have Windows, then everything is not so smooth:

The processor and the system bit capacity are indicated there, but very little is written about memory - only the volume. So you won't have much fun.
Find out detailed information about the components of your PC in the article -
Third party diagnostic apps
Space for work. Many third-party diagnostic utilities that can thoroughly determine everything, including the exact model of your boards and their location in the slots of the motherboard. It’s not possible to cover them all, so let’s consider at least a couple.
AIDA64
A diagnostic utility that is popular among many. Distributed in both free and commercial versions.

CPU-Z
The second most popular third-party application. It has the same intuitive interface, and in general duplicates the functions of the previous example, with the exception of a rather important detail - it has a portable version. You don't have to install it.
As in the previous case, in the program interface we look for the “Memory” and “SPD” items. In the drop-down list, we select information about which slot we want to view, and the program will immediately display all its characteristics. Everything, down to details like the serial number.

Ready! We hope these methods helped you find all the information you need. Good luck!
Video - How to find out what RAM is worth
Instructions
If possible, look at the markings printed directly on the module, or read the documentation included with the RAM. If you do not want to open the system unit and the documents are lost, use the capabilities of your system.
On your desktop or Start menu, right-click on the My Computer icon. Select "Properties" from the context menu. A new System Properties dialog box will open. Go to the “General” tab and find the “System” group. The amount of RAM is referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory).
You can also call the “System” component in another way: click the “Start” button or the Windows key, open the “Control Panel” and select the “System” icon in the “Performance and Maintenance” category by left-clicking on it.
The amount of memory can also be viewed through the task manager. Right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” from the drop-down menu or press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl, Alt and Del. In the window that opens, go to the “Performance” tab and read the information.
Another option: call the “Run” command through the “Start” menu or open the command line (“All Programs” - “Accessories” - “Command Prompt”) and enter systeminfo without any extra characters. Press Enter and wait for the information collection to complete. Read the information you need in the appropriate line.
In the “Start” menu, expand all programs, in the “Standard” folder, select the “System” subfolder and click on the “System Information” icon. A new window will open, select the first item in it with the left mouse button. Memory information is located towards the end of the data list.
From the desktop, press the F1 function key. The Help and Support Center window opens. In the search box, enter “RAM” without quotes. In the list generated by request, select the section “Get information about computer" and the task "Show general information about the system." After collecting information, look for the information you need in the “Memory (RAM)” section.
Sources:
- how to find information about your computer
Instructions
It is here, in the lower right corner, that you will see not only the type of your memory, but also the size of your RAM. RAM will be referred to as “RAM”, Random Access Memory. Random access memory, or “RAM”, is measured in gigabytes. So, for example, if your RAM value is shown as “1.49GB of RAM,” this will mean that you have “one and a half gigs of RAM” or one and a half gigabytes of RAM.
Video on the topic
Sources:
- how to see what RAM I have in 2018
Administrators and service center employees, when accepting a computer for repair, often ask the same question - whether the user has saved his personal data. But how to do this if you are new to using a computer and don’t know where to look for them? There are certain places where the operating system stores user data by default.

You will need
- - administrator rights.
Instructions
Open My Computer or any file manager you like. Go to drive “C:”. Find the Users folder on it or “Users” if your operating system is Russified. Go to this folder. Find the folder that matches your name or your account name. All files located in it relate to your work on computer- data from installed programs, documents, photographs, music and movies.
You can find your drawings in the “Images” folder, your documents in the “My Documents” folder, -files in the “My Videos” folder, and so on. Save files are stored in the "Save Games" folder - copy them if you plan to continue playing this game from the same place.
Pay attention to the “Desktop” folder. It contains everything that “lies” on your desktop. That is, shortcuts, folders, and individual files. Not on the desktop. Your personal information can also be stored in folders of installed programs in the Program Files directory, as well as in folders on drive C and other partitions. It is recommended to save copies of important documents to external media or an optical drive.
As a rule, for proper storage of data on a personal computer you need to create separate directories on your hard drive and folders so that all information matches the folder name. Additionally, store all important data on portable media so that in the event of system failures or your computer becoming infected with viruses, you can restore everything without any problems. Also, do not forget that computer Licensed software must be installed.
Video on the topic
Sources:
- how to find its data on a computer in 2019
Operational memory A computer is determined by the capacity of its random access memory (RAM). The amount of RAM of a personal computer determines its performance and the speed of processing incoming and outgoing information.

You will need
- Basic computer skills.
Instructions
In the menu that appears, find the line “Control Panel” and click on it once with the left mouse button.
In the "Control Panel" window that opens, find the "System" line and launch it by double-clicking on it with the left mouse button. The "System Properties" window will appear in front of you.
In the window that opens, open the “General” tab by left-clicking on it once.
Video on the topic
Useful advice
Most modern computers have the ability to increase the amount of RAM to the maximum allowed value. Increasing the amount of RAM is realized by connecting additional RAM cards, which are sold at any computer store.
Operational memory- This is space for temporary storage of data on chips, which is used by the computer to launch the operating system and run programs. RAM determines the speed of the computer, which is measured in MB (Megabytes) or GB (Gigabytes), the higher this indicator, the faster Windows and installed programs work.

Instructions
Video on the topic
Sources:
- How to find out what RAM is installed in your computer
Typically, users do not have enough system resources to complete work in applications. However, there are also the opposite situations - for working, for example, in older versions of Windows or testing programs in conditions of insufficient system resources, it may be necessary to reduce the amount of RAM.

You will need
- - screwdriver or screwdriver;
- - emulator program.
Instructions
Disconnect the computer from the power source. Using a screwdriver or screwdriver, unscrew the bolts from the system unit cover. Open the case and read the contents.
Find RAM. Usually the boards are thin long strips about 1.5-2 cm wide and about 10 long. If there is more than one strip, then unfasten all those that provide excess resources to perform the tasks you need. To do this, unfasten the fasteners on the sides and simply remove the memory from the motherboard socket.
Close the computer lid and secure it in position with screws. Turn on your computer. When the operating system boots, notice whether the speed has changed.
Open My Computer. In the area free of icons, right-click and select Properties. You will have various information about the system resources of the computer and operating system, see how much the RAM value has decreased. Close the windows.
Launch a program that was prevented from opening due to insufficient system resources. If it does not open, right-click on its shortcut, select “Properties”, check the box for compatibility mode with previous versions of the Windows operating system. At the same time, try to choose one that matches the release and relevance of your application.
If the previous steps do not help, use an emulator program for previous versions of the operating system. After installation, at the first launch, set all the necessary parameters and try to launch the application in emulator mode. If the program does not start, make sure that its copy is working, for example, try opening it on a computer with lower power levels.
Video on the topic
Please note
Try not to lose small fasteners when opening the computer case.
Useful advice
Before opening your computer, read the terms and conditions of the license agreement.
RAM significantly affects the performance of a computer, and sometimes it becomes necessary to install an additional memory module or replace one that has stopped working. You can completely cope with this yourself and do not contact specialists.

Instructions
In order to install RAM in your computer, you must first select memory that matches your motherboard if you have a system unit, or the technical characteristics of the model if you have a laptop. After you have purchased the RAM stick you need, you can begin installation.
To install memory in the system unit, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect all wires ( , mouse, LAN, speakers, power cord, etc.), and remove the left side cover of the system unit. To remove the cover, you will need to unscrew a few screws or loosen the latches.
2. Opening the left side cover will give you access to the contents of your . On the motherboard, find the RAM modules that match the ones you have and add a new memory stick, or replace the old one with a new one. As a rule, there are several on the motherboard where memory can be used, however, if one of the old modules fails, under no circumstances leave it on the board - the computer will not work!
3.Reassemble everything in reverse order and start the computer.
RAM is one of the main criteria for the normal performance and speed of a computer. It must be correctly matched to the PC processor. Otherwise, the system will not work at full capacity. If you want to increase the size of RAM, you should first check the existing one.

For computers running a 32-bit Windows operating system, there is an additional way to check the amount of RAM if you think it is more than 4 GB. This is due to the fact that such operating systems cannot display information correctly, and also do not use more than the specified size (this is a feature of their internal structure).
Download the free AIDA64 Extreme Edition application from the Internet and install it on your hard drive. It is with its help that you can see complete information about RAM modules. Launch the program. After the utility window appears, in the right part of it, left-click on the “Computer” section, and then select the “General Information” function. In the new tab you will see the “Motherboard” item. Click on it. In the program, the value next to the inscription “System memory” shows the size of the RAM in the context
Before improving the performance of your components, you need to know that by overclocking the processor, the user also overclocks the computer's RAM. It is advisable to overclock RAM through the BIOS, rather than the operating system, since in this case there will be much less hassle. In addition, before starting this procedure, it is advisable to read the instructions for the motherboard that is installed on the personal computer. Last but not least, failure to follow instructions can lead to disappointing consequences.
BIOS update
First, the user should update the BIOS. You can download and install the new BIOS version on a special website. The user can do otherwise and remove the battery from the motherboard for a few minutes, or use a special jumper, which is also located on the motherboard. It should be noted that this is done exclusively when the computer is turned off.
Overclocking RAM
When the BIOS is updated, you will need to open it using the Del button, which should be pressed before loading the operating system. In the window that appears, find the Advanced BIOS Features tab (Advanced or Power BIOS Features, depending on the motherboard used and BIOS version). In this tab, disable all Speed Spectrum parameters, that is, change the value to Disabled and use the F10 button to save the changes.
After the reboot, you need to go into this environment again, go to the Advanced item and find the DRAM Configuration item, and then go to the MemClock tab. The value should be reduced, for example, if the standard frequency is 667 MHz, then you will need to set it to approximately 533 MHz. You can find out at what frequency the memory operates using the Everest program. The changes are saved and the computer restarts.
Then again you need to go into the BIOS and find the HyperTransport Frequency item, and change its value from “AUTO” to x4 or x3. After restarting the BIOS, you will need to find the MB Intelligent Tweaker option. Here you need to go to the PCI-E Clock tab and set the frequency to 101 Mhz. Next, in the CPU Voltage Control item, set the voltage value to the standard one, which should be supplied to the processor by default. You can find out about this in the special documentation for the processor.
Next you need to open the CPU Clock Ratio menu and set the values to x9-11, and in the CPU Frequency or CPU Clock/Speed item you need to set the frequency. To do this, the nominal processor frequency must be divided by the multiplier that you set, and then you can find out how much to set the FSB bus (CPU Frequency). The acceleration begins right here. You need to do this little by little. You need to raise the FSB bus, the CPU Frequency (MHz) item from 10 to 15, from 15 to 20, etc.
After each change of this value, it is advisable to go to the operating system to work and check its performance. As a result, the system itself and the software installed on the computer should work faster.
This phrase is quite popular - RAM. Many people have heard about it and sometimes seen errors in the system associated with it, and they also write about it on many sites if you want to download a program or game. In this article you will learn almost everything you need and everything connected with it. I hope after reading there will be no more questions and you will become more literate.
I'll start from afar...
What is RAM?
RAM is a bar in or etc.
It turns out that if you disassemble the system unit (in this article I will focus on a PC, because it’s easier there), then you can visually see this bar (and sometimes there are several of them) and this is correct. It looks something like this:

in the laptop like this:

Thus, RAM is one of the “parts” of the computer. Moreover, one of the main ones, without which the computer cannot even boot.
By the way, RAM is also often called RAM, memory, RAM (Random Access Memory), RAM, etc.
What is RAM needed for?
To understand this, you need to pay attention to the first word.
The fact is that when the “brain” of a computer (central processor) accesses data on (and it accesses it almost constantly, because everything is stored there), it does this through an intermediary - our RAM.
The RAM acts as a kind of intermediary or buffer. When the processor needs something, it sends a command to RAM, and it already copies the information from the hard drive. Then the processor works only with the RAM, and when it finishes, the data is copied back to the hard drive.
Perhaps you will have a question: “So why is everything so complicated? Why use RAM if you can do it directly or handle it yourself?” The thing is that the hard drive only stores information, and if the processor also loaded it with the fact that it would need to work with it, then it would become terribly slow. Do we need it? Nope.
By the way, there is such a thing as Virtual Memory and Page File. You can read the article in more detail.
In short, I’ll just write that when there is little space left in the RAM (it’s constantly storing something in itself and new processes are running), it still turns to the hard drive (well, where can it go...) and takes it from there? place. True, this can slow down the computer.
Thus, some data is always stored in RAM. These can be the results of your actions in , and , and in , and in general everything is always “done” through RAM, as through an intermediary.
Another thing you should know here is that information is copied from the hard drive to RAM, then modified in it, and then sent back to the hard drive. The simplest and most common example of this is how you work with text documents.
You first open it, then modify it, and then save and close (or close and save). Do you understand what I'm getting at? Yes yes. You have worked with a document in RAM, and then you need to rewrite it, because... there is only an unmodified copy on disk.
By the way, this is why, in the event of a computer failure and emergency shutdown, you risk losing, in most cases, unsaved data. Just those that are currently in the RAM.
Types of RAM
As I wrote above, RAM is a special module that is built into a special connector on the motherboard. You can see what it looks like in the first picture above.
Of course, progress does not stand still. Today you can also find a hard drive that contains its own high-speed buffer to increase the speed of reading/writing information. There are also video cards with the same principle. Also, the RAM “slats” themselves can be equipped with special radiators to ensure the best heat transfer, which consequently affects performance.
But let's get back to the types... Now there are only two types - these are statistical And dynamic.
Statistical type of RAM (SRAM(Static random access memory)) is created on the basis of semiconductor triggers and has a very high operating speed. It has two disadvantages: high cost and takes up a lot of space. Therefore, it does not occur on desktop computers, or indeed in everyday life.
Dynamic type of RAM (DRAM(Dynamic random access memory)) is based on capacitors, therefore it has a high recording density and a relatively low cost. The disadvantages arise from the peculiarities of its design, namely, the use of small capacitors leads to rapid self-discharge of the latter, so their charge must be periodically replenished. This process is called memory regeneration, hence the name dynamic memory. Regeneration noticeably slows down the speed of its operation, so various intelligent schemes are used to try to reduce time delays.
Dynamic memory is also divided into generations. I won’t go into much history, I’ll just write that the third generation is widespread now DDR3 SDRAM which replaced DDR2(they are even still found on old computers to this day) and they are being prepared to replace them DDR4(but it won’t be soon, I think).
RAM capacity
This is the basic unit of measurement for RAM and is often used. Measured in megabytes (MB) and gigabytes (GB).
The most common question is How much RAM should I use? It all depends on two things:
1)
from what you will be doing. For example, for access to the Internet and simple work on a computer, 1GB may be enough. But it’s better to take it with a reserve and put at least 2 GB.
If you want to both play games and do graphics, then set it to 4 GB and higher.
For me, 4 GB is enough for everything. So my advice is 4GB of RAM and everything will be fine.
2)
depending on the bit depth of your operating system. Reading the article.
I’ll just write briefly that if it’s 32x, then no more than 4x. If 64x, then as many as you like.
Much also depends on your computer, in particular on the number and type of RAM connectors. Of course, you need to have enough connectors and the right type.
How to find out your computer's RAM
To see what kind of RAM you have, you can use two ways.
1)
Turn off the computer, open the system unit and remove the RAM stick. Next, we look at the sticker (sticker) on it and everything will be written there - the type and frequency and other information.
If it is not there, then at least determine the type from the picture:

2) Through a well-known utility CPU-Z, which can be downloaded from . On the tab Memory you can check basic information such as Type, Size, operating mode and timings used:

On the SPD tab you can see all the characteristics of a specific memory module installed in the selected slot:

I also want to write about the SPD tab that it contains information from the chip of the same name in the RAM. The manufacturer writes into it all the information about it (volume, labeling, manufacturer, serial number, recommended delays, etc.) and when the system boots, the computer reads all this information and sets the memory operating mode in connection with the settings contained in the chip.
How to clear RAM
As I wrote above, the RAM is increasingly loaded as the computer operates. If its volume is small, then it may be that the computer starts to slow down. Therefore, you should clear the RAM and then the computer will stop slowing down.
To clean, you can use the following methods:
1) Close unnecessary programs.
2) Wait a little. Windows has a utility utility for cleaning RAM. True, it doesn't always work.
3) Take advantage of special programs. I will not describe them, I will only write links to official sites:
4) Reboot
How to increase RAM
I think everything is very simple here. There is no way to increase it programmatically, only physically.
You just need to purchase the right bracket. Which one is needed? Read about this where it was written about volume.
I just want to add here that if, let’s say, you already have one 2 GB stick, and you want 4, then it’s better to take another one for 2 and have them work in parallel. Then they will have multi-threading and will be faster if you take out one at 2 and put 4 in its place.
Better to use in pairs.
I think that's all. If you haven’t written anything about RAM or what is not clear, write in the comments.
My respects dear site visitors. In the last article I wrote about. Now, having learned what it is and what and how it serves, many of you are probably thinking about purchasing a more powerful and productive RAM for your computer. After all, increasing computer performance with additional memory RAM is the simplest and cheapest (unlike, for example, a video card) method of upgrading your pet.
And... Here you are standing at the display case with packages of RAMs. There are many of them and they are all different. Questions arise: Which RAM should I choose?How to choose the right RAM and not make a mistake?What if I buy a RAM and then it doesn’t work? These are completely reasonable questions. In this article I will try to answer all these questions. As you already understand, this article will take its rightful place in the series of articles in which I wrote about how to choose the right individual computer components, i.e. iron. If you haven't forgotten, it included the following articles:
—
—
—
This cycle will continue, and in the end you will be able to assemble for yourself a super computer that is perfect in every sense 🙂 (if finances allow, of course :))
In the meantime learning how to choose the right RAM for your computer.
Let's go!
RAM and its main characteristics.
When choosing RAM for your computer, you must take into account your motherboard and processor because RAM modules are installed on the motherboard and it also supports certain types of RAM. This creates a relationship between the motherboard, processor and RAM.

Find out about what RAM does your motherboard and processor support? You can go to the manufacturer’s website, where you need to find the model of your motherboard, as well as find out which processors and RAM it supports. If you don’t do this, it will turn out that you bought a super modern RAM, but it is not compatible with your motherboard and will gather dust somewhere in your closet. Now let's move directly to the main technical characteristics of RAM, which will serve as unique criteria when choosing RAM. These include:
Here I have listed the main characteristics of RAM that you should pay attention to first when purchasing it. Now we will reveal each of them in turn.
Type of RAM.
Today, the most preferred type of memory in the world is memory modules DDR(double data rate). They differ in release time and, of course, technical parameters.
- DDR or DDR SDRAM(translated from English: Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory - synchronous dynamic memory with random access and double data transfer rate). Modules of this type have 184 contacts on the strip, are powered by a voltage of 2.5 V and have a clock frequency of up to 400 megahertz. This type of RAM is already obsolete and is used only in old motherboards.
- DDR2- a type of memory that is widespread at this time. It has 240 contacts on the printed circuit board (120 on each side). Consumption, unlike DDR1, is reduced to 1.8 V. The clock frequency ranges from 400 MHz to 800 MHz.
- DDR3- the leader in performance at the time of writing this article. It is no less common than DDR2 and consumes 30-40% less voltage compared to its predecessor (1.5 V). Has a clock frequency of up to 1800 MHz.
- DDR4- a new, super modern type of RAM, ahead of its counterparts both in performance (clock frequency) and voltage consumption (and therefore characterized by lower heat generation). Support for frequencies from 2133 to 4266 MHz is announced. At the moment, these modules have not yet entered mass production (they promise to release them into mass production in mid-2012). Officially, fourth generation modules operating in DDR4-2133 at a voltage of 1.2 V were presented at the CES exhibition by Samsung on January 4, 2011.
Amount of RAM.
I won’t write much about memory capacity. Let me just say that it is in this case that size matters :)
Just a few years ago, RAM of 256-512 MB satisfied all the needs of even cool gaming computers. Currently, for normal functioning of the Windows 7 operating system alone, 1 GB of memory is required, not to mention applications and games. There will never be too much RAM, but I’ll tell you a secret that 32-bit Windows uses only 3.25 GB of RAM, even if you install all 8 GB of RAM. You can read more about this.
Dimensions of the planks or the so-called Form factor.
Form - factor- these are the standard sizes of RAM modules, the type of design of the RAM strips themselves.
DIMM(Dual InLine Memory Module - a double-sided type of module with contacts on both sides) - mainly intended for desktop desktop computers, and SO-DIMM used in laptops.

Clock frequency.
This is a fairly important technical parameter of RAM. But the motherboard also has a clock frequency, and it is important to know the operating bus frequency of this board, since if you bought, for example, a RAM module DDR3-1800, and the motherboard slot (connector) supports the maximum clock frequency DDR3-1600, then the RAM module as a result will operate at a clock frequency of 1600 MHz. In this case, all sorts of failures, errors in the operation of the system, etc. are possible.

Note: Memory bus frequency and processor frequency are completely different concepts.

From the tables above, you can understand that the bus frequency, multiplied by 2, gives the effective memory frequency (indicated in the “chip” column), i.e. gives us the data transfer speed. The name tells us the same thing. DDR(Double Data Rate) - which means double the data transfer rate.
For clarity, I will give an example of decoding in the name of the RAM module - Kingston/PC2-9600/DDR3(DIMM)/2Gb/1200MHz, Where:
—Kingston- manufacturer;
- PC2-9600— name of the module and its capacity;
- DDR3(DIMM)— memory type (form factor in which the module is made);
— 2Gb— module volume;
- 1200MHz— effective frequency, 1200 MHz.
Bandwidth.
Bandwidth- a memory characteristic on which system performance depends. It is expressed as the product of the system bus frequency and the amount of data transferred per clock cycle. Throughput (peak data rate) is a comprehensive measure of capability RAM, it takes into account transmission frequency, bus width and the number of memory channels. The frequency indicates the potential of the memory bus per clock cycle - at a higher frequency, more data can be transferred.
The peak indicator is calculated using the formula: B=f*c, Where:
B is the bandwidth, f is the transmission frequency, c is the bus width. If you use two channels to transmit data, we multiply everything received by 2. To get a figure in bytes/s, you need to divide the result by 8 (since there are 8 bits in 1 byte).
For better performance RAM bus bandwidth And processor bus bandwidth must match. For example, for an Intel core 2 duo E6850 processor with a system bus of 1333 MHz and a bandwidth of 10600 Mb/s, you can install two modules with a bandwidth of 5300 Mb/s each (PC2-5300), in total they will have the system bus bandwidth (FSB) equal to 10600 Mb/s.
Bus frequency and bandwidth are denoted as follows: “ DDR2-XXXX" And " PC2-YYYY". Here "XXXX" denotes the effective memory frequency, and "YYYY" the peak bandwidth.
Timings (latency).
Timings (or latency)- these are time delays of the signal, which, in the technical characteristics of the RAM, are written in the form “ 2-2-2 " or " 3-3-3 "etc. Each number here expresses a parameter. In order it is always " CAS Latency"(working cycle time), " RAS to CAS Delay"(full access time) and " RAS Precharge Time» (pre-charge time).
Note
So that you can better understand the concept of timings, imagine a book, it will be our RAM that we access. Information (data) in a book (RAM) is distributed among chapters, and chapters consist of pages, which in turn contain tables with cells (like in Excel tables, for example). Each cell with data on the page has its own vertical (columns) and horizontal (rows) coordinates. To select a row, the RAS (Raw Address Strobe) signal is used, and to read a word (data) from the selected row (i.e., to select a column), the CAS (Column Address Strobe) signal is used. The full reading cycle begins with the opening of the “page” and ends with its closing and recharging, because otherwise the cells will be discharged and the data will be lost. This is what the algorithm for reading data from memory looks like:
- the selected "page" is activated by applying the RAS signal;
- data from the selected line on the page is transmitted to the amplifier, and a delay is required for data transmission (it is called RAS-to-CAS);
- a CAS signal is given to select a (column) word from that row;
- data is transferred to the bus (from where it goes to the memory controller), and a delay also occurs (CAS Latency);
- the next word comes without delay, since it is contained in the prepared line;
- after access to the row is completed, the page is closed, the data is returned to the cells and the page is recharged (the delay is called RAS Precharge).
Each number in the designation indicates how many bus cycles the signal will be delayed. Timings are measured in nanoseconds. The numbers can have values from 2 to 9. But sometimes a fourth one is added to these three parameters (for example: 2-3-3-8), called “ DRAM Cycle Time Tras/Trc” (characterizes the performance of the entire memory chip as a whole).
It happens that sometimes a cunning manufacturer indicates only one value in the RAM characteristics, for example “ CL2"(CAS Latency), the first timing is equal to two clock cycles. But the first parameter does not have to be equal to all timings, and may be less than others, so keep this in mind and do not fall for the manufacturer’s marketing ploy.
An example to illustrate the impact of timings on performance: a system with memory at 100 MHz with 2-2-2 timings has approximately the same performance as the same system at 112 MHz, but with 3-3-3 timings. In other words, depending on latency, the performance difference can be as much as 10%.
So, when choosing, it is better to buy memory with the lowest timings, and if you want to add a module to an already installed one, then the timings of the purchased memory must match the timings of the installed memory.
Memory operating modes.
RAM can operate in several modes, if of course such modes are supported by the motherboard. This single channel, two-channel, three-channel and even four-channel modes. Therefore, when choosing RAM, you should pay attention to this parameter of the modules.
Theoretically, the speed of the memory subsystem in dual-channel mode increases by 2 times, in three-channel mode – by 3 times, respectively, etc., but in practice, in dual-channel mode, the performance increase, unlike single-channel mode, is 10-70%.
Let's take a closer look at the types of modes:
- Single channel mode(single-channel or asymmetric) – this mode is activated when only one memory module is installed in the system or all modules differ from each other in memory capacity, operating frequency or manufacturer. It doesn’t matter what slots or memory you install into. All memory will run at the speed of the slowest memory installed.
- Dual Mode(dual-channel or symmetrical) - the same amount of RAM is installed in each channel (and theoretically the maximum data transfer rate is doubled). In dual-channel mode, memory modules work in pairs: 1st with 3rd and 2nd with 4th.
- Triple Mode(three-channel) – the same amount of RAM is installed in each of the three channels. Modules are selected according to speed and volume. To enable this mode, modules must be installed in slots 1, 3 and 5/or 2, 4 and 6. In practice, by the way, this mode is not always more productive than the two-channel one, and sometimes even loses to it in data transfer speed.
- Flex Mode(flexible) – allows you to increase the performance of RAM when installing two modules of different sizes, but the same operating frequency. As in dual-channel mode, memory cards are installed in the same connectors of different channels.
Generally, the most common option is dual-channel memory mode.
To operate in multi-channel modes, there are special sets of memory modules - the so-called Kit memory(Kit set) - this set includes two (three) modules, from the same manufacturer, with the same frequency, timings and memory type.
Appearance of KIT kits:
for dual channel mode

for three-channel mode

But the most important thing is that such modules are carefully selected and tested by the manufacturer itself to work in pairs (triples) in two- (three-) channel modes and do not imply any surprises in operation and configuration.
Manufacturer of modules.
Now on the market RAM Such manufacturers as have proven themselves well: Hynix, amsung, Corsair, Kingmax, Transcend, Kingston, OCZ…
Each company has its own for each product marking number, from which, if deciphered correctly, you can find out a lot of useful information about the product. Let's try to decipher the module marking as an example Kingston families ValueRAM(see image):

Explanation:
- KVR– Kingston ValueRAM i.e. manufacturer
- 1066/1333 – operating/effective frequency (Mhz)
- D3- memory type (DDR3)
- D (Dual) – rank/rank. A dual-rank module is two logical modules wired onto one physical channel and alternately using the same physical channel (needed to achieve the maximum amount of RAM with a limited number of slots)
- 4 – 4 DRAM memory chips
- R – Registered, indicates stable operation without failures or errors for as long a continuous period of time as possible
- 7 – signal delay (CAS=7)
- S– temperature sensor on the module
- K2– set (kit) of two modules
- 4G– the total volume of the kit (both slats) is 4 GB.
Let me give you another example of marking CM2X1024-6400C5:
From the labeling it is clear that this is DDR2 module volume 1024 MB standard PC2-6400 and delays CL=5.
Stamps OCZ, Kingston And Corsair recommended for overclocking, i.e. have the potential for overclocking. They will have small timings and a clock frequency reserve, plus they are equipped with radiators, and some even coolers for heat removal, because When overclocking, the amount of heat increases significantly. The price for them will naturally be much higher.
I advise you not to forget about fakes (there are a lot of them on the shelves) and buy RAM modules only in serious stores that will give you a guarantee.
Finally:
That's all. With the help of this article, I think you will no longer be mistaken when choosing RAM for your computer. Now you can choose the right RAM for the system and increase its performance without any problems. Well, for those who will buy RAM (or have already bought it), I will dedicate the following article, in which I will describe in detail how to install RAM correctly into the system. Don't miss...
Increasing RAM is one of the easiest ways to speed up your computer if you have problems with reloading pages in the browser, slow minimizing and maximizing applications, and other symptoms of low RAM. - a simple procedure that can be handled without contacting the service.
However, it is necessary not only to install, but also to correctly select new modules for purchase. RAM varies in type, frequency and capacity. Before purchasing new RAM modules, you need to find out what RAM is installed in your computer, select the appropriate one and purchase it.
Table of contents:How to choose replacement RAM
Choosing RAM to install in your computer is quite simple. There are two possible cases:

Most often, users add RAM to a computer, and they need to determine what memory is currently installed.
How to find out what RAM is installed in your computer
There are dozens of ways to determine the basic parameters of RAM installed in a computer. We will not consider all of them, and we will present below the most convenient and simple options for the average user.
Video instructions
Visual inspection
The easiest way to find out the basic parameters of the RAM installed in your computer is to inspect the already installed RAM module. To do this, you must first turn off the power to the computer, then remove the cover and pull out the bar (to remove it, you will need to loosen the clamps on both sides). There should be a sticker on it with key information about the RAM.

Advantages of a visual inspection:
- No need to turn on your computer or download third-party applications;
- In addition to the basic parameters of RAM, you can find out its exact model.
Disadvantages of visual inspection:
- If the sticker from the RAM has been torn off, the information cannot be found out;
- Some modern RAM modules do not have stickers with information attached to them due to the presence of a cooling radiator on them;
- This method is not suitable for laptops, since removing the cover from them is a very labor-intensive procedure.
Using BIOS
Through the BIOS or UEFI environment, you can determine the basic parameters of the RAM installed in the computer. To do this, before starting to load the operating system, that is, immediately after turning on the computer, press Del to go to the BIOS settings. Next you will have to act depending on the BIOS or UEFI version:

Advantages of determining RAM parameters using BIOS:
- You can obtain data even if Windows is not installed on the computer or does not load;
- If you need to check several RAM modules in a row to see if they are detected by the system, this method is the fastest.
Disadvantages of obtaining information about RAM using the BIOS:
- Since there are many BIOS versions, and most often they are not localized, it can be difficult to find information about RAM among the mass of parameters;
- The old BIOS does not always display all the necessary information, and often only the amount of RAM is visible.
Windows tools
The Windows operating system has built-in utilities that allow you to find out minimal information about RAM - its used volume. That is, it will not be possible to determine the memory type and frequency using operating system utilities.
There is another important limitation. Windows will only show the amount of memory used, not the total amount installed. This aspect should be taken into account if the computer is running 32-bit Windows, which does not support more than 3 GB of RAM. That is, if the computer has more RAM installed, it will not be displayed in diagnostic utilities, and the “extra” memory will not be used during operation.
There are several ways to find out the amount of RAM using Windows. The easiest way to do this is as follows:

Third party applications
A lot of diagnostic applications have been released for Windows, each of which can be used to solve specific problems. Most of them provide the ability to find out information about RAM. Below are examples of such programs that can be downloaded for free from developer sites to determine information about RAM.
CPU-Z
Information about RAM in the CPU-Z application is distributed across several tabs:

AIDA64
Another convenient application for viewing information about components installed on your computer is AIDA64. To find out information about RAM through the program, you need to select SPD in the “Motherboard” tab. The application determines all the main RAM parameters.