A universal device for working with information. Computer as a universal device for working with information (12 hours)
Presentation of a lesson on the topic "Computer as a universal device for working with information" for 8th grade. The development includes a brief lesson plan, a presentation to explain and initially reinforce new material, assignments for the lesson “Computer as a universal device for working with information” to reinforce the material in class and do homework.
Basic concepts of the lesson:
Computer,
CPU,
Information input devices,
Information output devices.
The main textbook is Semakin’s textbook, but to study the topic it is more convenient to use the presentation for the lesson and notebook materials with a printed basis according to Bosova’s program.
View document contents
“Computer as a universal device for working with information”
MAIN COMPUTER COMPONENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
COMPUTER AS A UNIVERSAL DEVICE FOR WORKING WITH INFORMATION

Keywords
- computer
- CPU
- memory
- input devices
- information output devices

Computer
A modern computer is a universal electronic program-controlled device for working with information.
A computer is called a universal device because it can be used for many purposes - process, store and transmit information, and be used by a person in different types of activities.

Computers can process different types of information: numbers, text, images, sounds.
Information of any kind is represented in a computer in the form of binary code.
Information
Coding principle
Natural numbers
Words
Remainders when divided by 2
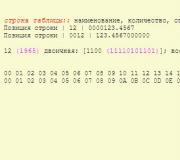
5: 2 = 2 rest. 1
2: 2 = 1 rest. 0
1: 2 = 0 rest. 1
Binary code
Coding table
a 11100001
b 11100010
i 11101001
t 11110100
Black and white image
Splitting an image into individual points
11100001 11101001 11110100
00000000 1111111 00000000
00000001 1111111 10000000
00000011 1111111 11000000

Software principle of computer operation
The computer processes data in accordance with program – a sequence of commands that must be executed on the data to solve the task.
Software controlled A computer is called a device because its operation is carried out under the control of programs installed on it.

Variety of modern computers
Any computer consists of a processor, memory, input and output devices.

Computer devices and their functions
The functions performed by computer devices are similar to the functions of a thinking person.
information storage
Memory devices
CPU
Input devices
Output devices
information processing
receiving information
transfer of information

Information flow diagram
Input devices
Internal
memory
External
memory
Output devices
CPU
Computer processor
Computer internal memory
RAM
Persistent memory
Processor QAX
Intel processor

External computer memory
Streamers
Magnetic memory
Disk drives
NGMD
NMJD
Optical memory
USB Card
Map
memory
Electronic memory
Flash Drive
USB Drives


The most important
Modern computer - a universal electronic program-controlled device for working with information.
Any computer consists of from:
- processor
- memory
- information input and output devices.
The functions performed by these devices are in some ways similar to those of a thinking person.

Questions and tasks
What is the essence of the software principle of a computer?
What human capabilities are reproduced by a computer?
Label the main components of a computer according to the principles of von Neumann architecture.
Why is a modern computer called a universal electronic program-controlled device?
List the main types of devices included in a computer.
What is the purpose of the processor?
Add the missing inscriptions to the information flow diagram on your computer:
What is binary data?
What is a computer program?
External
memory
Internal
memory

Supporting notes
Computer - universal electronic software
a controlled device for working with information.
Computer
Devices
storage
Device
processing
Devices
input and output
Magnetic
memory
CPU
Keyboard
Optical
memory
Monitor
Printer
Electronic
memory
Software processing of data on a computer DATA Numerical, textual, graphic and audio information can be processed by a computer if it is presented in a binary sign system. Information in binary computer code, i.e. data is a sequence of zeros and ones. it is information that is processed by a computer into binary computer code.

PROGRAMS In order for the computer to “know” what to do with the data, how to process it, it must receive a certain command (instruction). Typically, the solution to a problem is presented in the form of an algorithm, i.e. a certain sequence of commands. Such a sequence of commands (instructions), written in a language “understandable” to the computer, is called a program. A program is a sequence of commands that a computer executes while processing data.


Computer Architecture Computer architecture is a description at some general level that includes the logical organization and resources of a computer. The computer architecture is based on 2 principles: 1. Modular – backbone principle; 2. John von Neumann's principle.

A computer is an indivisible, integral object. It consists of a number of devices - modules. And all the modules are connected to each other through a set of electronic lines - a backbone that ensures data exchange between all devices. Modular - main principle



Information through input devices or by reading from long-term memory devices through the information highway enters RAM; the processor retrieves it, processes it and puts it back; the results are reported to the user through output devices or stored in the computer's long-term memory.

Input Devices Input devices are designed to convert human-readable information into computer-readable information. Manipulators (mouse, joystick, trackball, touchpad, graphics tablet); Keyboard; Microphone; Scanner; Digital photos – video cameras.



INTRODUCTION
THEMATIC PLANNING ON THE TOPIC “Computer as a universal device for working with information” OF INFORMATION SCIENCE COURSE IN 7TH CLASS.
CONCLUSION
APPLICATION
INTRODUCTION
Our present time is characterized by a high pace of human life, constant variability of the world around us, and the all-consuming and widespread use of information technology in all areas of activity. It is difficult to underestimate the role of fundamental education aimed at forming an individual capable of living in these conditions, ready to constantly master new technologies.
Computer science, as a natural science discipline, is very important in achieving the goals of school education. The knowledge acquired by students on the basis of computer science finds its application in the study of other subject areas, as well as in real life situations.
The topic “Computer as a universal device for working with information”, studied in the 7th grade of the school computer science course, is of great practical importance. Students should develop an idea of the main components of a computer, their functions, and the idea that a computer is a universal information processing device.
The purpose of the work is to develop thematic planning on the above topic of the computer science course in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard. Achieving this goal requires solving the following tasks: determining the structure of thematic planning, determining the place and role of the section in the general computer science course, studying the main elements of the content of the topic, determining the planned results of studying the topic: subject, meta-subject and personal universal learning activities, developing practical assignments on this topic in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard.
DESCRIPTION OF THE DEVELOPED THEMATIC PLANNING AND PRACTICAL WORK ON THE TOPIC.
The section “Computer as a universal device for working with information” is studied in the 7th grade after students become familiar with the topic “Information and information processes.” In the developed thematic planning, the total number of hours on the topic under consideration is 7 hours. Planning proceeds according to the structure of the presentation of the material in the textbook"Informatics 7"authorsBosova L.L., Bosova A.Yu. The result of the work on this topic was the development of a practical assignment for the lesson “Files and file structures” in the context of the Federal State Educational Standard [Appendix].
The content of the lesson topic is presented as follows:organizational moment, thenthe studied material is checked according to the questions in §2.3; visual check of homework completion in the workbook, determination of the purpose and topic of the lesson. In process andlearning new materialStudents can be recommended to organize viewing of the “Files and Folders” animation. The lesson material can be presented using the presentation “Files and File Structures” from the electronic supplement to the textbook. As you review the lesson content, it is recommended that you complete the assignments in the workbook. The developed practical work should be offered at stage 3consolidation of new material. After which the lesson ends with a stage of control and reflection.
The essence of practical work at the computer is as follows: students are asked to build a file structure based on this model, then “arrange” several files with names 1, 2, etc., based on their contents in the created folders. The folders have appropriate names. To do this, you need to determine the location of each file, that is, in which folder it should be placed. Files with the extensionJPEGare pictures, the topics are taken from the content of paragraphs 2.1-2.3 previously studied by students. For example, students should place files No. 4 and No. 5, which describe the external and internal memory of the computer, in a folder called “Computer Memory,” and file No. 11 about service programs should be placed in the “System Software” folder. As a result of this work, students will learn how to create a directory tree, delete, copy and move files.
Thus, in addition to consolidating skills in working with files and file structure, students’ knowledge acquired in previous lessons is updated, namely about the main components of a computer, its structure, and computer software.
2. THEMATIC PLANNING ON THE TOPIC “Computer as a universal device for working with information” OF INFORMATION SCIENCE COURSE IN 7TH CLASS.
Lesson numberLesson topic
Planned results
Textbook paragraph
Subject
Meta-subject and personal
11.
Basic computer components and their functions.
Students will learn to analyze computer devices from the point of view of organizing procedures for input, storage, processing, output and transmission of information;
Cognitive: extract information, navigate their knowledge system and realize the need for new knowledge, make a preliminary selection of information sources to search for new knowledge.
Regulatory: they determine the goal of educational activity with the help of the teacher and find the means of its implementation.
Communicative: listen to others, try to accept a different point of view, are ready to change their minds.
Personal: assess the importance of education and learning new things.
§ 2.1
12.
Personal computer.
Learn to name the elements of the internal and external structure of a computer.
Cognitive: plan their own activities.
Regulatory: determine the goal, problem in educational and life-practical activities.
Communicative: they are active in interaction to solve communicative and cognitive problems.
Personal: maintain motivation for learning activities.
§ 2.2
13.
Computer software.
Students study the composition of computer software and the main characteristics of the operating system.
Cognitive: independently search for the necessary information, use models and diagrams to solve cognitive problems.
Regulatory: accept and maintain the learning task, plan their actions.
Communicative: express their point of view, construct statements and judgments.
Personal: develop a respectful attitude towards the point of view of another person.
§ 2.3
14.
Files and file structures. Practical work.
Learn to perform basic operations with files and folders.
Cognitive: find reliable information necessary to solve assigned problems, recognize various systems, and identify essential features.
Regulatory: determine the goal, problem, work according to plan, find and correct errors.
Communicative: make their own decisions and make assumptions, listen to each other’s arguments.
Personal: make mutual concessions in various situations of the educational process.
§ 2.4
15.
User interface.
Define the concept of user interface and name the main elements of the graphical interface.
Cognitive: independently form cognitive goals, search and select the necessary information.
Regulatory: determine the goal of educational activity and find the means of its implementation.
Communicative: interact with each other in educational activities, participate in a collective discussion of the problem.
Personal: determine their personal position, develop a friendly attitude towards other people.
§ 2.5
16.
Generalization and systematization of the basic concepts of the topic “Computer as a universal device for working with information.”
They learn to define the basic concepts of the topic and work with the textbook.
Cognitive: search and select the necessary information.
Regulatory: formulate educational goals when studying a topic.
Communicative: participate in group discussion of posed problems.
Personal: develop a friendly attitude towards other people.
§ 2.1- § 2.5
17.
Test No. 2. Computer as a universal device for working with information.
Students develop skills in working with text materials and learn to find the correct answer to the question posed.
Cognitive: structure their knowledge.
Regulatory: organize work according to plan, show persistence in achieving goals.
Communicative: take initiative in finding and solving problems.
Personal: understand the need for education, assessment of knowledge and determine their personal position.
CONCLUSION
The proposed thematic planning and practical work as part of one of the lessons corresponds to the main provisions of the federal state educational standard for basic general education. As a result of the application of this planning, students develop universal learning actions, namely: Lpersonal learning activities: the student’s ability to establish connections between the goal of educational activity and its motive, i.e. between the result of the teaching and what motivates the activity, for the sake of which it is carried out, thus, a meaningful organization of the student’s own activity must be carried out. Regulatory UUD:goal setting as setting an educational task based on the correlation of what is already known and learned by the student and what is still unknown, planning - determining the sequence of intermediate goals taking into account the final result, control in the form of comparing the method of action and its result with a given standard in order to detect deviations and differences from the standard.Communicative UUD: planning educational cooperation with the teacher and peers, i.e. determining the purpose of cooperation, the functions of participants, methods of interaction, the ability to express one’s thoughts with sufficient completeness and accuracy in accordance with the tasks and conditions of communication, mastery of monologue and dialogic forms of speech in accordance with the grammatical and syntactic norms of the native language, the ability to prove one’s own opinion. Cognitive UUD:analysis of objects in order to identify features (essential, non-essential); putting forward hypotheses and their substantiation; building a logical chain of reasoning, proof; subsuming the concept; drawing conclusions; establishing cause-and-effect relationships, structuring knowledge; synthesis as the composition of a whole from parts, including independently completing, replenishing the missing components; selection of bases and criteria for comparison and classification of objects.
LIST OF SOURCES USED
Federal state educational standard of basic general education.
Approximate basic educational program of an educational institution.Basic school / [comp. E. S. Savinov]. - M.: Education, 2011.
Computer science: textbook for grade 7 / L.L. Bosova, A.Yu. Bosova. – 5th ed. – M.: BINOM. Knowledge Laboratory, 2016.
Computer science: workbook for grade 7 / L.L. Bosova, A.Yu. Bosova. – 3rd ed. – M.: BINOM. Knowledge Laboratory, 2015.
INTERNET SOURCES
http://metodist.lbz.ru/authors/informatika/3/eor7.php